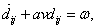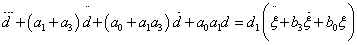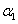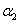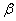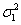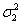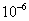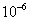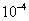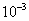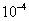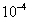Chapter 12. Vehicle control considering road conditions
Two types of road disturbances are distinguished: stochastic (random) irregularities and deterministic disturbances.
-
Random road unevenness is characterized by its stochastic properties and can be regarded as disturbances of long or infinite duration. Deterministic road disturbance is mostly related to an excitation of short duration such as kerbs, speed humps and potholes. An accurate representation of the stochastic road irregularities is required in order to predict vehicle responses to road excitations, see [128], [129].
-
The stochastic description of road surfaces is useful for calculating average performance parameters, but such calculations do not account for the deterministic effect of road damage, obstacles and potholes, or for the high degree of regularity in road profiles that occasionally are present due to terrain features, road building practices or repeated traversal by vehicles.
A very simple model for the vertical road is a colored noise resulting from the application of a first-order shaping filter to a white noise signal. This process is given by the following differential equation:
|
|
(12) |
where 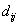 is the road displacements at the respective springs,
is the road displacements at the respective springs, 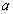 is a coefficient depending on the shape of the road irregularities and
is a coefficient depending on the shape of the road irregularities and 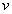 is the forward vehicle speed. The parameter
is the forward vehicle speed. The parameter 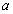 needed for the considered road description is selected as follows:
needed for the considered road description is selected as follows: 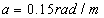 in asphalt,
in asphalt, 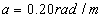 in concrete and
in concrete and 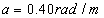 in rough.
in rough.
In order to classify different roads Hac has proposed a parameter based method, where the road signal was given by the following continuous time model, see [130]:
|
|
(13) |
where 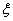 is a white noise process, parameters
is a white noise process, parameters 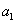 ,
,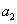 ,
,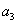 ,
,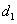 ,
,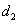 ,
,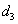 depend of the forward velocity and the road type. The calculation of the parameters are the following:
depend of the forward velocity and the road type. The calculation of the parameters are the following:
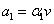
, 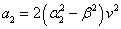 ,
, 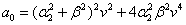 ,
,
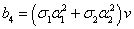
, 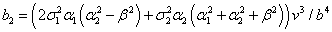 ,
,
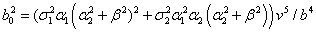
,
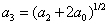
, 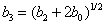 ,
, 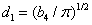 .
.
The relation between the characteristics that describe the road quality and the parameters defining the road model are given in Table 3.
|
Road Type |
|
|
|
|
|
|
asphalt |
0.2 |
0.05 |
0.6 |
7.65 |
1.36 |
|
paved |
0.5 |
0.2 |
2.0 |
2.55 |
4.5 |
|
dirt |
0.8 |
0.5 |
1.1 |
7.5 |
2.5 |
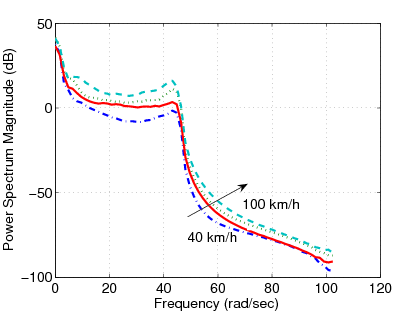
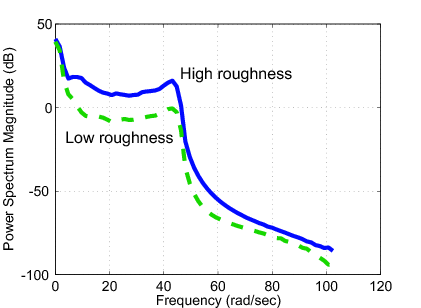
Using the measured data the effects of the forward velocity to the suspension system is illustrated in Figure 149. The effects of the road roughness to the suspension system when the velocity of the vehicle is 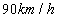 are shown in Figure 150.
are shown in Figure 150.