|
CIE
|
acronym of the International Commission on Illumination, derived from the French name: Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage
|
Nemzetközi Világítástechnikai Bizottság, CIE
|
A Nemzetközi Világítástechnikai Bizottság francia nevéből (Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage) képezett betűszó
|
|
background, single stimulus
|
region surrounding the stimulus subtending approximately 10º
|
háttér, elsődleges inger
|
Az ingert körülvevő, mintegy 100 kiterjedésű környezet
|
|
CIE 1964 standard colorimetric observer
|
ideal observer whose colour-matching properties correspond to the CIE colour-matching functions 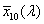 , , 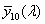 , , 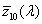 adopted by the CIE in 1964 adopted by the CIE in 1964
See also ISO 11664-1:2007(E)/CIE S 014-1/E:2006 Colorimetry - Part 1: CIE Standard Colorimetric Observers
|
CIE 1964 szabványos színmérő észlelő
|
Az az ideális észlelő, amelynek színinger-megfeleltető tulajdonságai megegyeznek az
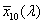 , , 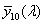 , , 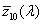 CIE színinger-megfeleltető függvényekkel. CIE színinger-megfeleltető függvényekkel.
Lásd még az ISO 11664-1:2007(E)/CIE S 014-1/E:2006 Colorimetry - Part 1: CIE Standard Colorimetric Observers szabványban.
|
|
CIE 1976 uniform-chromaticity-scale diagram
|
uniform chromaticity scale diagram produced by plotting in rectangular coordinates v′ against u′, quantities defined by the equations:
u′ = 4 X / (X + 15Y + 3Z) = 4x / (-2x + 12y + 3)
v′ = 9 Y / (X + 15Y + 3Z) = 9y / (-2x +12y + 3)
where X, Y, Z are the tristimulus values in the CIE 1931 or 1964 standard colorimetric systems, and x, y are the corresponding chromaticity coordinates of the colour stimulus considered
Equivalent term: “CIE 1976 UCS diagram”
NOTE This diagram is a modification of, and supersedes, the CIE 1960 UCS diagram in which v was plotted against u in rectangular coordinates. The relationships between the 2 pairs of coordinates are:
u′ = u; v′ = 1,5 v.
|
CIE 1976 szabványos színességi skálájú diagram
|
Az alábbi összefüggések szerint számított
u' és v' derékszögű koordinátákkal értelmezett egyenletes színességi skálájú diagram:
u¢ = 4 X / (X + 15Y + 3Z) = 4x / (-2x + 12y + 3)
v¢ = 9 Y / (X + 15Y + 3Z) = 9y / (-2x +12y + 3)
ahol X, Y, Z a kiválasztott színinger színinger-összetevői a CIE 1931 vagy a CIE 1964 kiegészítő rendszerben és x, y a megfelelő színességi koordináták.
Egyenértékű fogalom: CIE 1976 UCS diagram.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A korábban használt u és v és az új u' és v' koordinátapár közötti összefüggés:
u¢ = u; v¢ = 1,5 v.
|
|
CRI (abbreviation)
|
See “colour rendering index”
|
CRI
(rövidítés)
|
Lásd „színvisszaadási index”
|
|
fovea centralis
|
See “fovea”
|
fovea centralis
|
lásd “fovea”
|
|
GRL (abbreviation)
|
See “glare rating limit”
|
GRL
(rövidítés)
|
lásd „Káprázási határ”
|
|
object colour
|
colour perceived as belonging to an object
|
tárgy szín
|
egy tárgyhoz tartozó színészlelet
|
|
object mode (of colour appearance)
|
colour seen as ascribed to an object
|
tárgyszín szemlélet
(színészlelet)
|
tárgyszín szemléletű színmegjelenés
|
|
spectral chromaticity coordinates [r(λ), g(λ), b(λ); x(λ), y(λ), z(λ); r10(λ), g10(λ), b10(λ); x10(λ), y10(λ), z10(λ)]
|
chromaticity coordinates of monochromatic stimuli
|
Spektrumszín koordináták[r(λ), g(λ), b(λ); x(λ), y(λ), z(λ); r10(λ), g10(λ), b10(λ); x10(λ), y10(λ), z10(λ)]
|
Monokromatikus színingerek színinger koordinátái
|
|
visual field
|
See “field of vision”
|
Látótér
|
lásd „látómező”
|
|
psychophysical colour
|
specification of a colour stimulus in terms of operationally defined values, such as the tristimulus values
NOTE 1 When the meaning is clear from the context the term “colour” can be used alone.
NOTE 2 In German, “Farbe” is often used instead of “Farbempfindung”. The use of “Farbe” in the sense of “Farbvalenz” should be avoided. It is only when the sense is obvious from the context, or when “Farbempfindung” and “Farbvalenz” are equally suitable, that “Farbe” may be used in the sense of “Farbvalenz”.
See also “colour”
|
(pszihofizikai) szín
|
színingerek meghatározása a színészlelés mechanizmusa alapján, pl tristimulusos módon
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
amennyiben a „szín” szó a szövegkörnyezet alapján világosan érthető, önmagában is alkalmazható.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A német nyelvben gyakran használják a „Farbe” szót a „Farbempfindung” helyett. A “szín” szó használata “Farbvalenz” értelemben viszont kerülendő. Ez csak akkor elfogadott, ha a szövegkörnyezet alapján teljesen egyértelmű a jelentése, vagy ha a “Farbempfindung” és a “Farbvalenz” egyformán megfelelő, akkor használható a “Farbe” szó “Farbvalenz“értelemben.
Lásd még “colour”, azaz “szín”
|
|
lightness (of a related colour)
|
brightness of an area judged relative to the brightness of a similarly illuminated area that appears to be white or highly transmitting
NOTE Only related colours exhibit lightness.
|
viszonylagos világosság, relatív világosság
|
adott felület világossága egy hozzá hasonlóan megvilágított, fehérnek vagy nagyon fényáteresztőnek látszó felületnek a világosságához képest.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
Csak viszonyított színnek lehet „világosság”-a
|
|
CIE 1976 u′, v′ chromaticity difference [Δc]
|
difference between 2 colour stimuli, defined as the Euclidean distance between the points representing them nt he u′, v′ chromaticity diagram and calculated as equation:
Δc = [(Δu′)2 + (Δv′)2]1/2
|
CIE 1976 u′, v′
szerinti színkülönbség
[
Δ
c]
|
két színinger különbsége a színingerek színpontjainak Euclidesi távolságaként értelmezve az u’, v’ színezeti diagramban a következő formula szerint:
Δc = [(Δu′)2 + (Δv′)2]1/2
|
|
eight degree geometry
|
irradiation or measurement of reflecting materials at 8° to the normal, at one azimuth angle
NOTE 1 This geometry is used to substitute the 0° directional geometry in many practical applications of reflection measurements, as it permits differentiation between specular component included and excluded measurements
NOTE 2 This geometry is restricted to measurements using an integrating sphere as described in CIE 15 Colorimetry
See also CIE 15 Colorimetry (section 5)
|
8°-os geometria
|
Fényvisszaverő anyagok sugárzása vagy mérése a felület normálisához képest 80-os szögben, egy bizonyos azimutszög irányában
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ez a geometria helyettesítheti a 0 °-os geometriát reflexiós mérések esetén, mivel lehetővé teszi a tükrös komponens kizárását.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ez a geometria nem alkalmazható a CIE 15 Kolorimetria című fejezetben leírt integráló gömbbel történő mérésnél
Lásd még: CIE 15 Colorimetry (5. rész)
|
|
amplitude of fluctuation of the luminous flux (of a source run on alternating current)
|
relative amplitude of the periodic fluctuation of the luminous flux as measured by the ratio of the difference between the maximum and the minimum instantaneous luminous flux, Φ
max
and Φ
min
respectively, to the sum of both of these values:
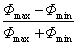
Unit: 1
NOTE 1 This ratio is usually expressed in % and is then known under the expression “percent flicker” which, however, should be deprecated.
NOTE 2 Another means sometimes used by the lighting industry to characterize the fluctuation in light output is “flicker index”, which is defined by the ratio of 2 areas deduced from the diagram representing the variation of the instantaneous flux over a period of time; the area of the diagram above the average value is divided by the total area under the curve (this total area is the product of the average value and the given period of time).
|
a fényáram ingadozás amplitudója (változóárammal táplált fényforrás)
|
periodikus fényáram ingadozás relatív amplitudója a fényáram maximális és minimális értéke különbségeként mérve, (Φ
max
and Φ
min
), és viszonyítva ugyanezen értékek összegéhez:
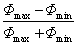
Egysége: 1
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ezt az értéket gyakran %-ban szokták megadni, és “fikker százalék”-nak szokták nevezni, de ez már elavult elnevezés.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Másrészt a világítástechnikai szakmában “flicker index” néven gyakran a fény fluktuációjának két terület arányával történő jellemzésére használják olymódon, hogy a fényáram változások diagramján az átlagértéket osztják a teljes görbe alatti területtel (a teljes görbe alatti terület az átlag és az adott időtartam szorzata).
|
|
Abney phenomenon
|
change of hue produced by decreasing the purity of a colour stimulus while keeping its dominant wavelength and luminance constant
|
Abney jelenség
|
A színezet megváltozása, ha a színérzékelési inger színinger-tisztasága csökken, míg ez alatt domináns hullámhossza és fénysűrűssége állandó.
|
|
Abney's law
|
empirical law stating that if 2 colour stimuli, A and B, are perceived to be of equal brightness and 2 other colour stimuli, C and D, are perceived to be of equal brightness, then the additive mixtures of A with C and B with D will also be perceived to be of equal brightness
NOTE The validity of Abney's law depends strongly on the observing conditions.
|
Abney- törvénye
|
Az a tapasztalati törvény, amely szerint, ha az A és B színinger egyforma világosságú, valamint a C és a D színinger is egyforma világosságú, akkor az A és a C, valamint a B és a D additív színinger keveréke is egyforma világosságú.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
Az Abney törvény érvényessége jentősen függ a megfigyelési körülményektől.
|
|
adaptation
|
process by which the state of the visual system is modified by previous and present exposure to stimuli that may have various luminance values, spectral distributions and angular subtenses
NOTE Adaptation to specific spatial frequencies, orientations, sizes, etc. is recognized as being included in this definition.
|
adaptáció
|
Az a folyamat, amely során a látórendszer tulajdonságai alkalmazkodnak az egymást követő — fénysűrűségben, spektrális eloszlásban és látószögben különböző — fényingerekhez.
MEGJEGYZÉSEK:
Használatosak a világosra adaptált és sötétre adaptált kifejezések, az elsőt mondják, ha a fénysűrűség legalább néhány kandela per négyzetméter, a másodikat pedig; ha a fénysűrűség néhány század kandela per négyzetméternél kisebb.
A térbeli frekvenciákra, irányítottságokra, méretekre stb. való adaptáció beletartozik ebbe a definícióba.
|
|
adaptation, state of
|
state of the visual system after an adaptation process has been completed
NOTE The terms “light adaptation” and “dark adaptation” are also used, the former when the luminances of the stimuli are of at least 10 cd·m-2, and the latter when the luminances are of less than some hundredths of a cd·m-2.
|
adaptációs állapot
|
a látórendszer állapota, amikor egy adaptációs folyamat teljesen befejeződött
MEGJEGYZÉS:
Használatos a „világos adaptáció” és a „sötét adaptáció” kifejezés is, az előbbi akkor, ha az inger világossága legalább 10 cd·m-2, és az utóbbi akkor, ha kevesebb, mint néhány század CD·m-2.
|
|
white, adapted
|
colour stimulus that an observer who is adapted to the viewing environment would judge to be perfectly achromatic and to have a luminance factor of unity
NOTE The colour stimulus that is considered to be the adapted white may be different at different locations within a scene.
|
fehér adaptációs színészlelet
|
olyan színinger, amelyet egy, a környezethez adaptált megfigyelő tökéletesen fehérnek és a világossági tényezőjét egységnyinek ítél meg.
MEGJEGYZÉS az adaptációs fehérnek tekintett színinger a látvány különböző területein különböző lehet.
|
|
adapted white
|
See “white, adapted”
|
Fehér adaptációs pont
|
Lásd „fehérpont,adaptációs
(színmegjelenítési modellnél)”
|
|
adaptive colour shift
|
change in the perceived colour of an object caused solely by change of chromatic adaptation
|
adaptációs színeltolódás
|
Egy tárgy színének csak a kromatikus adaptáció megváltozása által okozott változása.
|
|
adaptive colorimetric shift
|
mathematical adjustment in chromaticity and luminance factor of an object colour stimulus to correct for a change in chromatic adaptation
|
adaptációs színeltolódás
|
A szín inger színének vagy világosságának matematikai korrekciója a szín adaptáció megváltoztatása céljából
|
|
accommodation
|
adjustment of the dioptric power of the crystalline lens by which the image of an object, at a given distance, is focused on the retina
|
akkomodáció
|
A szemlencse törőerejének megváltozása, aminek következtében egy adott távolságban lévő tárgy képe a retinán képződik le.
|
|
achromatic colour
|
1. in the perceptual sense: perceived colour devoid of hue
NOTE The colour names white, grey and black are commonly used or, for transmitting objects, colourless and neutral.
2. in the psychophysical sense: see “achromatic stimulus”
|
akromatikus szín
|
Észlelet értelemben: színészlelet, amelynek nincs színezete.
Megnevezésében általában a fehér, szürke és fekete vagy fényáteresztő tárgyakra vonatkozóan a színtelen és semleges neveket használják.
|
|
achromatic stimulus
|
stimulus that, under the prevailing conditions of adaptation, gives rise to an achromatic perceived colour
NOTE In the colorimetry of object colours, the colour stimulus produced by the perfect reflecting or transmitting diffuser is usually considered to be an achromatic stimulus for all illuminants, except for those whose light sources appear to be highly chromatic.
|
akromatikus színinger
|
Olyan színinger, amely — általános adaptációs feltételek mellett — akromatikus színészleletet hoz létre.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A tárgy színének észlelésében a tökéletesen visszaverő vagy áteresztő testet minősítik akromatikusnak minden sugárzáseloszlásra, kivéve, ha a sugárzás eloszlás nagyon kromatikusnak látszik.
|
|
reference colour stimuli
|
set of 3 colour stimuli on which a trichromatic system is based
NOTE 1 These stimuli are either real colour stimuli or theoretical stimuli which are defined by linear combinations of real colour stimuli; the magnitude of each of these 3 reference colour stimuli is expressed in terms of either photometric or radiometric units, or more commonly by specifying the ratios of their magnitudes or by stating that a specified additive mixture of these stimuli matches a specified achromatic stimulus.
NOTE 2 In the CIE standard colorimetric systems, the reference colour stimuli are represented by the symbols [R], [G], [B]; [X], [Y], [Z]; [R10], [G10], [B10] and [X10], [Y10], [Z10].
|
szín észlelési alap ingerek
|
Az a három színinger, amelyen a trikromatikus rendszer alapul.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ezek valós vagy elméleti színingerek, az elmélet i színingereket valós színingerek lineáris kombinációjával értelmezik; a három alapszíningert fotometriai vagy radiometriai egységekben fejezik ki; szokásos csak értékeik arányát megadni, vagy úgy értel mezni azokat, hogy a három alapszíninger meghatározott additív keveréke egy adott akromatikus színinger legyen.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Az alapszíningerek jelei a CIE színmérő rendszerekben [R], [G], [B]; [X], [Y], [Z] és [X10], [Y10], [Z10].
|
|
basic colour names
|
group of eleven colour names found in anthropological surveys to be in wide use in fully developed languages: white, black, red, green, yellow, blue, brown, grey, orange, purple, pink
|
alapszínek neve
|
antropológiai megfigyelések alapján meghatározott 11 szín megnevezés, amelyeket a legfejlettebb nyelvekben széles körben alkalmaznak: fehér, fekete, vörös, zöld, sárga, kék, barna, szürke, narancs , lila, rózsaszín
|
|
unique hue
|
hue that cannot be further described by the use of hue names other than its own
Equivalent term: “unitary hue”
NOTE There are 4 unique hues: red, green, yellow and blue forming 2 pairs of opponent hues: red and green, yellow and blue.
|
alapszínezet
|
Színezet, amelyet csak a saját színezetének megfelelő névvel szabad leírni.
azonos értelemben: „ős szín”
MEGJEGYZÉS:
4 „ős szín” van: vörös, zöld, sárga, kék, melyek két kiegészítő színpárt alkotnak: vörös és zöld, sárga és kék.
|
|
unitary hue
|
See “unique hue”
|
alapszínezet
|
|
|
alychne
|
surface in tristimulus space that represents the locus of colour stimuli of zero luminance
NOTE This surface passes through the origin of the space. It intersects any chromaticity diagram in a straight line which is also called the alychne; this line lies wholly outside the domain of chromaticities bounded by the spectrum locus and the purple boundary.
|
alychne
|
A nulla fénysűrűségű színingereket tartalmazó felület a trikromatikus színtérben.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ez a felület átmegy a trikromatikus tér kezdőpontján. Bármely színinger-diagrammal való metszete egyenes vonal, ennek szintén alychne a neve; ez a vonal teljesen kívül fekszik a spektrumgörbe és a btborvonal által értelmezett színesség tartományán.
|
|
anomalous trichromatism
|
See NOTE 1 to “defective colour vision”
|
anomális trichromatizmus
|
Lásd az „anomális trichromatizmus” címszónál az 1. MEGJEGYZÉS-t.
|
|
aperture colour
|
perceived colour for which there is no definite spatial localisation in depth, such as that perceived as filling a hole in a screen
|
apertura színészlelet
|
Színészlelet, amelynek nincs a térben mélységbeli kiterjedése, amint ez például egy ernyőn lévő nyílás esetében érzékelhető.
|
|
Bezold-Brücke phenomenon
|
change of hue produced by changing the luminance (within the range of photopic vision) of a colour stimulus while keeping its chromaticity constant
NOTE 1 With certain monochromatic stimuli, hue remains constant over a wide range of luminances (for a given condition of adaptation). The wavelengths of these stimuli are sometimes referred to as “invariant wavelengths”.
NOTE 2 With increasing intensity, below 500 nm hues shift more toward blue, and above 500 nm hues shift more toward yellow (reds become yellower with increasing brightness).
|
Bezold-Brücke jelenség
|
A színezet megváltozása, ha a színérzékelési inger fénysűrűsége megváltozik (a fotopos látási tartományban), míg a színessége állandó.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Vannak monokromatikus szín ingerek, amelyek színezete állandó marad széles fénysűrűségi tartományban (egy adott adaptációs állapotban). Ezeknek a színérzékelési ingereknek a hullámhosszait invariáns hullámhosszaknak nevezik.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Növekvő intenzitás esetén, 500 nm hullámhossz alatti színeknél a kék felé tolódik, 500 nm-en túl a sárga felé tolódik (a vörösek sárgásabbá válnak növekvő világosság esetén).
|
|
purple stimulus
|
stimulus that is represented in a chromaticity diagram by a point lying within the triangle defined by the point representing the specified achromatic stimulus and the 2 ends of the spectrum locus which correspond approximately to the wavelengths 380 nm and 780 nm
NOTE Purple is a hue which is not represented in the hues of the spectrum.
|
bíbor színinger
|
olyan színinger, amelynek színpontja a színességi diagram monokromatikus színeket ábrázoló vonalának 380 nm-nél és 780 nm-nél található végpontjait összekötő egyenesen található.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
a bíbor szín nem található meg a spektrum színek (monokromatikus színek) között.
|
|
purple boundary
|
line in a chromaticity diagram, or the plane surface in a tristimulus space, that represents additive mixtures of monochromatic stimuli of wavelengths approximately 380 nm and 780 nm
|
bíborvonal
|
olyan vonal a színességi diagramban illetőleg a tristimulusos színtér egy sík felületén, amely a közelítőleg 380 nm-es és a 780 nm-es monokromatikus ingerek additív keverésével áll elő.
|
|
CIE 1931 standard colorimetric observer
|
ideal observer whose colour-matching properties correspond to the CIE colour-matching functions 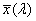 , , 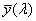 , , 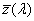 adopted by the CIE in 1931 adopted by the CIE in 1931
|
CIE 1931 szabványos színmérő észlelő
|
Az az ideális észlelő, amelynek színinger- megfelel tető tulajdonságai megegyeznek az 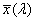 , , 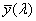 , ,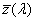 CIE színinger-megfeleltető függvényekkel. CIE színinger-megfeleltető függvényekkel.
|
|
CIE 1931 standard colorimetric system [X, Y, Z]
|
system for determining the tristimulus values of any spectral power distribution using the set of reference colour stimuli [X], [Y], [Z] and the 3 CIE colour-matching functions  , , 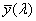 , , 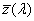 adopted by the CIE in 1931 adopted by the CIE in 1931
NOTE 1 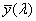 is identical to V(λ) and hence the tristimulus values Y are proportional to values of luminance. is identical to V(λ) and hence the tristimulus values Y are proportional to values of luminance.
NOTE 2 This standard colorimetric system is applicable to centrally-viewed fields of angular subtense between about 1° and about 4° (0,017 rad and 0,07 rad).
NOTE 3 The CIE 1931 standard colorimetric system can be derived from the CIE 1931 RGB colorimetric system using a transformation based on a set of 3 linear equations. The CIE 1931 RGB system is based on 3 real monochromatic reference stimuli.
See also CIE 15 Colorimetry
|
CIE 1931 szabványos színmérő rendszer [X, Y, Z]
|
Olyan trikromatikus rendszer, amely a CIE által elfogadott [X], [Y], [Z] alapszíningereken és az 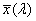 , , 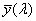 , , 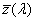 színinger- megfeleltető függvényeken alapul (lásd a CIE 15. sz. kiadványát), és amely alkalmas tetszőleges spektrális teljesítmény- eloszlások színinger-összetevőinek meghatározására. színinger- megfeleltető függvényeken alapul (lásd a CIE 15. sz. kiadványát), és amely alkalmas tetszőleges spektrális teljesítmény- eloszlások színinger-összetevőinek meghatározására.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Az 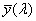 megegyezik a V(l) láthatósági függvénnyel és ennek következtében a Y színinger-összetevő arányos a fénysűrűséggel. megegyezik a V(l) láthatósági függvénnyel és ennek következtében a Y színinger-összetevő arányos a fénysűrűséggel.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ezt a színmérő rendszert kell használni a központi látásra a látómező 1° és kb. 4° (0,017 és 0,07 rad) között területén.
3. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A CIE 1931 szabványos színmérő rendszer a CIE 1931 RGB színmérő rendszerből származtatható, 3 lineáris egyenleten alapuló transzformáció által. A CIE 1931 RGB színmérő rendszer 3 tényleges monokromatikus referencia színingeren alapul. Lásd még CIE 15 Colorimetry.
|
|
CIE 1964 uniform colour space
|
3-dimensional, approximately uniform colour space produced by plotting in rectangular coordinates U*, V*, W* quantities defined by the equations:
W* = 25 Y1/3 - 17
U* = 13 W* (u - un)
V* = 13 W* (v - vn)
NOTE 1 Y, u, v describe the colour stimulus considered, and un, vn describe a specified white achromatic stimulus, where u = u′, 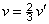 ; ; 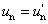 , , 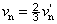 . .
See also “CIE 1976 uniform chromaticity scale diagram”
NOTE 2 The difference between 2 stimuli, ΔE*, is defined as the Euclidean distance between the points representing them in U*V*W* space and calculated as:
ΔE* = [(ΔU*)2 + (ΔV*)2 + (ΔW*)2]1/2.
NOTE 3 This colour space is obsolete (except that it is still used in the calculation of colour rendering index). The currently recommended object colour spaces are CIELAB and CIELUV.
|
CIE 1964 egyenletes színtér
|
3-dimenziós, közelítőleg egyenletes színtér, amely a z U*, V*, W* mennyiségek derékszögű koordinátarendszerében az alábbi egyenletekkel definiálható:
W* = 25 Y1/3 - 17
U* = 13 W* (u - un)
V* = 13 W* (v - vn)
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Y, u, v a megfelelő színingert, míg
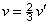 ; ; 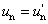 , , 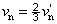 . .
a fehér akromatikus ingert írja le.
Lásd még “CIE 1976 egyenletes skálázású színességi diagram”.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Két inger ΔE* különbsége az U*V*W* térben Euklidesi különbségként értelmezhető az alábbiak szerint:
ΔE* = [(ΔU*)2 + (ΔV*)2 + (ΔW*)2]1/2.
3. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ez a színtér már elavult, (kivéve a színvisszaadási index számítására alkalmazzák). A jelenleg ajánlott színtér a CIELAB és a CIELUV.
|
|
CIE 1964 standard colorimetric system [X10, Y10, Z10]
|
system for determining the tristimulus values of any spectral power distribution using the set of reference colour stimuli [X10], [Y10], [Z10] and the 3 CIE colour-matching functions 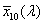 , , 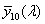 , , 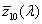 adopted by the CIE in 1964 adopted by the CIE in 1964
NOTE 1 This standard colorimetric system is applicable to centrally-viewed fields of angular subtense greater than about 4° (0,07 rad).
NOTE 2 When this system is used, all symbols that represent colorimetric measures are distinguished by use of the subscript 10.
See also CIE 15 Colorimetry
|
CIE 1964 szabványos színmérő rendszer
[X10, Y10, Z10]
|
Olyan trikromatikus rendszer, amely a CIE által elfogadott [X10], [Y10], [Z10] alap színingereken és az 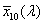 , , 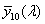 , , 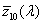 színinger-megfeleltető függvényeken alapul (lásd a CIE 15. sz. kiadványát), és amely alkalmas tetszőleges spektrális teljesítmény eloszlások színinger-összetevőinek meghatározására. színinger-megfeleltető függvényeken alapul (lásd a CIE 15. sz. kiadványát), és amely alkalmas tetszőleges spektrális teljesítmény eloszlások színinger-összetevőinek meghatározására.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ezt a CIE színmérő rendszert kell használni, ha a centrális látás látómezeje nagyobb, mint kb, 4° (0,07 rad).
2 MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ha ezt a rendszert használják a színmérésben, minden mennyiséghez ki kell írni a 10 indexet.
A Y10 értékek nem arányosak a fénysűrűséggel.
Lásd még CIE 15 Colorimetry
|
|
CIE 1974 special colour rendering index [Ri]
|
measure of the degree to which the psychophysical colour of a CIE test colour sample illuminated by the test illuminant conforms to that of the same sample illuminated by the reference illuminant, suitable allowance having been made for the state of chromatic adaptation
See also CIE 13 Method of Measuring and Specifying Colour Rendering of Light Sources
|
CIE 1974 egyedi színvisszaadási
index [Ri]
|
Mérőszám annak jellemzésére, hogy egy adott CIE tesztelő színmintának a vizsgált fényforrással kapott színe hogyan egyezik meg ugyanazon mintának referencia sugárzáseloszlással történő megvilágítás hatására kapott színével, figyelembe véve a kromatikus adaptációt.
Lásd még CIE 13 Method of Measuring and Specifying Colour Rendering of Light Sources
|
|
CIE 1974 general colour rendering index [Ra]
|
mean of the CIE 1974 special colour rendering indices for a specified set of 8 test colour samples
See also CIE 13 Method of Measuring and Specifying Colour Rendering of Light Sources
|
CIE 1974 általános színvisszaadási index
|
Nyolc meghatározott CIE 1974 tesztelő színmintára számított CIE 1974 egyedi színvisszaadási index átlaga.
|
|
CIE 1976 L*a*b* colour difference [
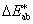 ]
]
|
difference between 2 colour stimuli defined as the Euclidean distance between the points representing them in the L*a*b* space and calculated as:
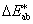 = [(ΔL*)2 + (Δa*)2 + (Δb*)2]1/2 = [(ΔL*)2 + (Δa*)2 + (Δb*)2]1/2
Equivalent term: “CIELAB colour difference”
See also CIE 15 Colorimetry
See also ISO 11664-4:2008(E)/CIE S 014-4/E:2007 Colorimetry - Part 4: CIE 1976 L*a*b* Colour Space
|
CIE 1976 L*a*b* színkülönbség
|
Két színinger közötti különbség, amely az L*, a*, b* koordinátarendszerben értelmezett térbeli távolság és amelyet a következő egyenlet szerint lehet számítani:
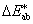 = [(DL*)2 + (Da*)2 + (Db*)2]1/2 = [(DL*)2 + (Da*)2 + (Db*)2]1/2
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A CIE 1976 a, b színezeti különbséget a következőképpen lehet számítani;
CIE 1976 a,b színezeti különbség;
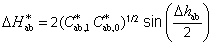
Lásd még: CIE 15 Colorimetry
Lásd még: ISO 11664-4:2008(E)/CIE S 014-4/E:2007 Colorimetry - Part 4: CIE 1976 L*a*b* Colour Space
|
|
CIE 1976 L*a*b* colour space
|
3-dimensional, approximately uniform colour space produced by plotting in rectangular coordinates L*, a*, b* quantities defined by the equations:
L* = 116 f (Y/Yn) - 16
a* = 500 [f (X/Xn) - f (Y/Yn)]
b* = 200 [f (Y/Yn) - f (Z/Zn)]
where
f (X/Xn) = (X/Xn)1/3 if (X/Xn) > (6/29)3
f (X/Xn) = (841/108) (X/Xn) + 4/29
if (X/Xn) ≤ (6/29)3
and
f (Y/Yn) = (Y/Yn)1/3 if (Y/Yn) > (6/29)3
f (Y/Yn) = (841/108) (Y/Yn) + 4/29 if (Y/Yn) ≤ (6/29)3
and f (Z/Zn) = (Z/Zn)1/3
if (Z/Zn) > (6/29)3
f (Z/Zn) = (841/108) (Z/Zn) + 4/29
if (Z/Zn) ≤ (6/29)3
and X, Y, Z describe the colour stimulus considered
and Xn, Yn, Zn describe a specified white achromatic stimulus.
Equivalent term: “CIELAB colour space”
NOTE Approximate correlates of lightness, chroma and hue may be calculated as follows:
CIE 1976 lightness
L* = 116 f (Y/Yn) - 16
where
f (Y/Yn) = (Y/Yn)1/3 if (Y/Yn) > (6/29)3
f (Y/Yn) = (841/108) (Y/Yn) + 4/29
if (Y/Yn) ≤ (6/29)3
CIE 1976 a, b chroma
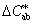 = ( a*2 + b*2)1/2 = ( a*2 + b*2)1/2
CIE 1976 a, b hue angle
hab = arctan (b*/a*)
See also CIE 15 Colorimetry
See also ISO 11664-4:2008(E)/CIE S 014-4/E:2007 Colorimetry - Part 4: CIE 1976 L*a*b* Colour Space
|
CIE 1976 L*a*b* színtér
|
Megközelítően egyenletes, háromdimenziós színtér, amelynek L*a*b* derékszögű koordinátáit a köv. egyenletek határozzák meg:
L* = 116 f (Y/Yn) - 16
a* = 500 [f (X/Xn) - f (Y/Yn)]
b* = 200 [f (Y/Yn) - f (Z/Zn)]
ahol
f (X/Xn) = (X/Xn)1/3
ha (X/Xn) > (6/29)3
f (X/Xn) = (841/108) (X/Xn) – 4/29
ha (X/Xn) ≤ (6/29)3
és
f (Y/Yn) = (Y/Yn)1/3
ha (Y/Yn) > (6/29)3
f (Y/Yn) = (841/108) (Y/Yn) + 4/29 ha
(Y/Yn) ≤ (6/29)3
és f (Z/Zn) = (Z/Zn)1/3
ha (Z/Zn) > (6/29)3
f (Z/Zn) = (841/108) (Z/Zn) + 4/29
ha (Z/Zn) ≤ (6/29)3
és X, Y, Z a választott színingert határozza meg
és Xn, Yn, Zn a meghatározott fehér akromatikus színingert határozza meg
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A világossági tényezővel, krómával és színezettel megközelítően megfelelő mennyiségek:
CIE 1976 világossági tényező:
L* = 116 f (Y/Yn) - 16
ahol
f (Y/Yn) = (Y/Yn)1/3
ha (Y/Yn) > (6/29)3
f (Y/Yn) = (841/108) (Y/Yn) +4/29
ha (Y/Yn) ≤ (6/29)3
CIE 1976 a, b króma
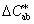 = ( a*2 + b*2)1/2 = ( a*2 + b*2)1/2
CIE 1976 a, b színezeti szög
hab = arctan (b*/a*)
Lásd még: CIE 15 Colorimetry
Lásd még: ISO 11664-4:2008(E)/CIE S 014-4/E:2007 Colorimetry - Part 4: CIE 1976 L*a*b* Colour Space
|
|
CIE 1976 L*u*v* colour difference [
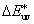 ]
]
|
difference between 2 colour stimuli, defined as the Euclidean distance between the points representing them in the L*u*v* space and calculated as equation:
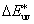 = [(ΔL*)2 + (Δu*)2 + (Δv*)2]1/2 = [(ΔL*)2 + (Δu*)2 + (Δv*)2]1/2
Equivalent term: “CIELUV colour difference”
See also CIE 15 Colorimetry
See also ISO 11664-5:2009(E)/CIE S 014-5/E:2009 Colorimetry - Part 5: CIE 1976 L*u*v* Colour Space and u', v' Uniform Chromaticity Scale Diagram
|
CIE 1976 L*u*v* színkülönbség
|
Két színinger közötti különbség, amely az L*u*v* koordinátarendszerben értelmezett térbeli távolság és amelyet a (3) egyenlet szerint kell számítani:
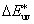 = [(DL*)2 + (Du*)2 + (Dv*)2]1/2 = [(DL*)2 + (Du*)2 + (Dv*)2]1/2
Azonos meghatározás a CIE 1976 u,v színezeti különbség, amelyet a következőképpen lehet számítani:
CIE 1976 u,v színezeti különbség:
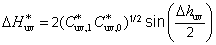
Dhuv = huv,1 - huv,0.
L. a CIE 15.2 sz. kiadványát.)
|
|
CIE 1976 L*u*v* colour space
|
3-dimensional, approximately uniform colour space produced by plotting in rectangular coordinates L*, u*, v* quantities defined by the equations:
L* = 116 f (Y/Yn) - 16
u* = 13 L* (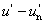 ) )
v* = 13 L* (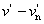 ) )
where
f (Y/Yn) = (Y/Yn)1/3 if (Y/Yn) > (6/29)3
f (Y/Yn) = (841/108) (Y/Yn) + 4/29 if (Y/Yn) ≤ (6/29)3
and Y, u′, v′ describe the colour stimulus considered
and Yn, 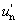 , , 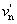 describe a specified white achromatic stimulus describe a specified white achromatic stimulus
Equivalent term: “CIELUV colour space”
NOTE Approximate correlates of lightness, saturation, chroma, and hue may be calculated as follows:
CIE 1976 lightness
L* = 116 f (Y/Yn) - 16
where
f (Y/Yn) = (Y/Yn)1/3 if (Y/Yn) > (6/29)3
f (Y/Yn) = (841/108) (Y/Yn) + 4/29 if (Y/Yn) ≤ (6/29)3
CIE 1976 u, v saturation
suv = 13 [(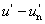 )2 + ( )2 + (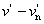 )2]1/2 )2]1/2
CIE 1976 u, v chroma
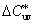 = ( u*2 + v*2)1/2 = L* suv = ( u*2 + v*2)1/2 = L* suv
CIE 1976 u, v hue angle
huv = arctan [(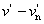 ) / ( ) / (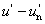 )]= arctan (v*/ u*) )]= arctan (v*/ u*)
See also CIE 15 Colorimetry
See also ISO 11664-5:2009(E)/CIE S 014-5/E:2009 Colorimetry - Part 5: CIE 1976 L*u*v* Colour Space and u', v' Uniform Chromaticity Scale Diagram
|
CIE 1976 L*u*v* színtér
|
Megközelítően egyenletes, három dimenziós színinger tér, amelynek L*, u*, v* derékszögű koordinátáit a következő egyenletek határozzák meg:
L* = 116 f (Y/Yn) - 16
u* = 13 L* (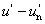 ) )
v* = 13 L* (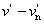 ) )
ahol
f (Y/Yn) = (Y/Yn) 1/3 ha (Y/Yn) > (6/29)3
f (Y/Yn) = (841/108) (Y/Yn) + 16/116 ha (Y/Yn) ≤ (6/29)3
és Y, u¢, v¢ a kiválasztott színinger
és Yn, 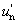 , , 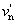 a fehér akromatikus színingert határozza meg a fehér akromatikus színingert határozza meg
Egyenértékű definició: „CIELUV színtér”
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A világossági tényezőnek, a telítettségnek, krómának és színezetnek megközelítően megfelelő mennyiségek a következők:
CIE 1976 világossági tényező:
L* = 116 f (Y/Yn) - 16 ,
ahol
f (Y/Yn) = (Y/Yn)1/3 ha (Y/Yn) > (6/29)3
f (Y/Yn) = (841/108) (Y/Yn) + 4/29 ha (Y/Yn) ≤ (6/29)3
CIE 1976 u,v telítettség:
suv = 13 [(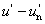 )2 + ( )2 + (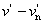 )2]1/2 )2]1/2
CIE 1976 u,v króma:
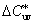 = ( u*2 + v*2)1/2 = L* suv = ( u*2 + v*2)1/2 = L* suv
CIE 1976 u,v színezeti szög:
huv = arctan [(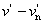 ) / ( ) / (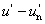 )]= arctan (v*/ u*) )]= arctan (v*/ u*)
Lásd még a CIE 15.2 sz. kiadványát
Lásd még
ISO 11664-5:2009(E)/CIE S 014-5/E:2009 Colorimetry - Part 5: CIE 1976 L*u*v* Colour Space and u', v' Uniform Chromaticity Scale Diagram
|
|
CIE colour-matching functions
|
functions 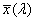 , , 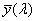 , , 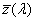 , in the CIE 1931 standard colorimetric system or , in the CIE 1931 standard colorimetric system or 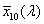 , , 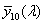 , , 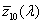 , in the CIE 1964 standard colorimetric system , in the CIE 1964 standard colorimetric system
See also “CIE standard colorimetric observer”, “CIE 1931 standard colorimetric observer” and “CIE 1964 standard colorimetric observer”
See also CIE 15 Colorimetry
See also ISO 11664-1:2007(E)/CIE S 014-1/E:2006 Colorimetry - Part 1: CIE Standard Colorimetric Observers
|
CIE 1976 színegyeztető függvény
|
A CIE 193 1 színmérő rendszerében a 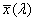 , , 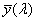 , , 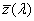 függvényeknek a CIE 1964 kiegészítő színmérő rendszerben megfelel az függvényeknek a CIE 1964 kiegészítő színmérő rendszerben megfelel az 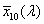 , , 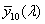 , ,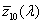 függvény függvény
Lásd még „CIE szabványos színmérő észlelő”, „CIE 1931 szabványos színmérő észlelő”, „CIE 1964 szabványos színmérő észlelő”. Lásd még a CIE 15. sz. kiadványát). Lásd még az ISO 11664-1:2007(E)/CIE S 014-1/E:2006 Colorimetry – 1 Rész:CIE Szabványos színmérő észlelő
|
|
CIE 1976 UCS diagram
|
See “CIE 1976 uniform chromaticity scale diagram”
|
CIE 1976 UCS diagram
|
Lásd „CIE 1976 szabványos színességi skálájú diagram”
|
|
CIE standard deviate observer
|
standard observer whose colour-matching functions deviate from those of the CIE standard colorimetric observer in a defined manner
NOTE 1 The defined deviations can be applied to the CIE 1931 standard colorimetric observer or the CIE 1964 standard colorimetric observer.
NOTE 2 The use of the standard deviate observer is intended to generate differences that are typical of those that occur when colour matches are made by different real observers whose colour vision is classified as normal.
See also CIE 80-1989
|
CIE szabványostól eltérő észlelő
|
Olyan színmérő észlelő, akinek a színmegfeleltető függvényei eltérnek a CIE szabványos színmérő észlelő színmegfeleltető függvényeitől.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Az adott eltérést a CIE 1931 szabványos színmérő észlelőhöz vagy a CIE 1964 szabványos színmérő észlelőhöz képest lehet értelmezni.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A CIE szabványostól eltérő észlelő fogalom alkalmazásához célszerű a szabványos színmérő észlelő és az adott különböző normál színmérő észlelők különbségét képezni.
|
|
CIE standard colorimetric observer
|
standard colorimetric observer defined by the CIE colour-matching functions
See also “CIE colour-matching functions”
|
CIE szabványos színmérő észlelő
|
Az a CIE szabványos színmérő észlelő, akinek színlátása a CIE színmegfeleltető függvények alapján van meghatározva. Lásd még „CIE színmegfeleltető függvények”.
|
|
CIELAB colour space
|
See “CIE 1976 L*a*b* colour space”
|
CIELAB színinger
|
Lásd „CIE 1976 L*a*b* színtér”
|
|
CIELAB colour difference [
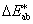 ]
]
|
See “CIE 1976 L*a*b* colour difference”
|
CIELAB színinger különbség
|
Lásd „CIE 1976 L*a*b* színkülönbség”
|
|
CIELUV colour space
|
See “CIE 1976 L*u*v* colour space”
|
CIELUV színinger
|
Lásd „CIE 1976 L*u*v* színtér”
|
|
CIELUV colour difference [
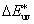 ]
]
|
See “CIE 1976 L*u*v* colour difference”
|
CIELUV színinger különbség
|
Lásd „CIE 1976 L*u*v* színkülönbség”
|
|
cones
|
photoreceptors in the retina containing light-sensitive pigments capable of initiating the process of photopic vision
|
csapok
|
Azok a retinában lévő, fényérzékeny pigmenteket tartalmazó fényérzékelő receptorok, amelyek lehetővé teszik a világosban (fotopos) látást.
|
|
D illuminant
|
See “daylight illuminant”
|
D megvilágítás
szabványos nappali fény
|
Lásd „nappali fény”
|
|
deutan
|
See NOTE 2 to “defective colour vision”
|
deután
|
Lásd 2. MEGJEGYZÉS a „színtévesztés”-nél
|
|
deuteranomaly
|
See NOTE 3 to “defective colour vision”
|
deuteranomál
|
Lásd 3. MEGJEGYZÉS a „színtévesztés”-nél
|
|
deuteranopia
|
See NOTE 4 to “defective colour vision”
|
deuteranópia
|
Lásd 4. MEGJEGYZÉS a „színtévesztés”-nél
|
|
dichromatism
|
See NOTE 5 to “defective colour vision”
|
dikromatizmus
|
Lásd 5. MEGJEGYZÉS a „színtévesztés”-nél
|
|
equivalent veiling luminance (for disability glare)
|
luminance that, when added by superposition to the luminance of both the adapting background and the object, makes the luminance threshold or the luminance difference threshold the same under the two following conditions: (1) glare present, but no additional luminance; (2) additional luminance present, but no glare
|
egyenértékű fátyol fénysűrűség
|
Az a fénysűrűség, amelyet mind az adaptáció állapotát meghatározó háttér fénysűrűségéhez, mind a tárgy fénysűrűségéhez hozzá kell adni, hogy a rontó káprázás nélküli fénysűrűség-különbség küszöbértéke megegyezzék a rontó káprázás állapotát jellemző tényleges küszöbértékkel.
|
|
equivalent contrast (of a task)
|
luminance contrast of a visibility reference task having equal visibility at the same luminance level as that of the task considered
See also “contrast”
|
Egyenértékű kontraszt
|
Egy olyan referencia látványnak a kontrasztja, amely ugyanolyan kontrasztúnak látszik, mint az adott látvány.
Lásd még: „kontraszt”
|
|
uniform point source
|
See NOTE to “point source”
|
egyenletes fénysűrűségű égbolt
|
Lásd a MEGJEGYZÉS-t a „Pontszerű fényforrás”-nál
|
|
UCS diagram
|
See “uniform chromaticity scale diagram”
|
UCS diagram
|
Lásd „egyenletes színességi skálájú diagram”
|
|
uniform chromaticity scale diagram
|
2-dimensional diagram in which the coordinates are defined with the intention of making equal distances represent as nearly as possible equal steps of colour discrimination of colour stimuli of the same luminance throughout the diagram
Equivalent term: “UCS diagram”
|
egyenletes színinger tér
|
olyan 2-dimenziós diagram, amelynek koordinátáit úgy definiálják, hogy azokon azonos megvilágítás mellett egyenlő távolságokhoz lehetőség szerint azonos színkülönbségi lépések tartozzanak az egész diagramban
Egyenértékű definició: „UCS diagram”
|
|
conventional retinal illuminance
|
product of the luminance in a specified direction and the apparent area of the pupil (natural or artificial) seen from that direction
Unit: cd, cd⋅m-2⋅mm2, troland
|
Egyezményes retina megvilágítás
|
Adott irányból és a természetes vagy mesterséges pupilla adott területén át érkező megvilágítás.
Mértékegysége: cd, cd⋅m-2⋅mm2, troland
|
|
primary light source
|
surface or object emitting light by a transformation of energy
|
elsődleges fényforrás
|
Olyan felület vagy test, amely energia átalakulás eredményeként fényt bocsát ki.
|
|
resultant colour shift
|
combined illuminant colour shift and adaptive colour shift
|
eredő színérzéklet eltolódás
|
A sugárzáseloszlás és a kromatikus adaptáció okozta szín eltolódás kombinációja.
|
|
resultant colorimetric shift
|
combined illuminant colorimetric shift and adaptive colorimetric shift
|
eredő színmérési eltolódás
|
A sugárzás eloszlás okozta és az adaptációs színmérési eltolódás eredője (vektora).
|
|
perceptual attribute correlate
|
fundamental uni-variate colour description or metric
|
érzékelés szerinti jellemző
|
alapvetően egyváltozós színmeghatározás vagy mértékegység
|
|
hemeralopia
|
anomaly of vision in which there is a pronounced inadequacy or complete absence of scotopic vision
Equivalent term: “night blindness”
|
Farkasvakság, hemeralópia
|
Látási rendellenesség; a szkotopos látás nagyon gyenge vagy teljesen hiányzik.
|
|
veiling luminance (for disability glare)
|
luminance that superimposes on the retinal image and reduces the contrast by stray light in the eye
Unit: cd·m-2
|
fátyol fénysűrűség
|
Megvilágítás, amely hozzáadódik a retinális képhez, és ez által csökkenti a szembe érkező fény kontrasztját.
Mértékegysége: cd·m-2
|
|
veiling glare (imaging)
|
light, reflected from an imaging medium, that has not been modulated by the means used to produce the image
NOTE 1 Veiling glare lightens and reduces the contrast of the darker parts of an image.
NOTE 2 The veiling glare is sometimes referred to as “ambient flare”.
|
fátyolkáprázás (képalkotó rendszeré)
|
reflektált fény, amely nem hordozza a képi információt
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A fátyolkáprázás megvilágítja a kép sötét részeit és ezáltal csökkenti a kép kontrasztját.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A fátyolkáprázást szokták háttér fátyolnak is nevezni.
|
|
veiling reflections
|
specular reflections that appear on the object viewed and that partially or wholly obscure the details by reducing contrast
|
fátyolreflexió
|
Olyan tükrös reflexió, amely a szemlélt tárgyon jelenik meg és részben vagy teljesen elhomályosítja a részleteket, lecsökkentve a kontrasztot.
|
|
white point, adopted (colour appearance model)
|
computational reference white point (the white point used in the computation, e.g. the adopted white point or the display illuminant white point) used by a colour appearance model
NOTE 1 A white point used by a colour appearance model is an adopted white point.
NOTE 2 The adopted white point may or may not be the adapted white point, and one of the most common applications of an adopted white point is to achieve an optimally reproduced device white. For example, an adopted white point corresponding to a given medium may be used in place of an adapted white point in order that no colorants are used to create a white.
NOTE 3 The concept of adopted white point applies to both colour appearance models and reproduction models.
|
fehérpont, adaptációs
(színmegjelenítési modellnél)
|
számítástechnikai referencia-fehér pont (A számításokhoz alkalmazott fehér pont, például a képen kijelölt fehér pont, vagy a képernyő egy világos, fehér pontja) amelyet a színmegjelenítési modellhez használunk.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Felvett vagy névleges fehér pont egy fehér pont, amelyet a színmegjelenítési modellnél használunk.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A felvett vagy névleges fehér pont lehet az a fehér pont, amelyhez adaptálunk, és a felvett vagy névleges fehér pont leginkább szokásos alkalmazása az optimális reprodukciós fehér pont elérése.
3. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A felvett vagy névleges fehér pontot egyaránt alkalmazzák a szín megjelenítési modellnél és a reprodukciós modellnél.
|
|
conspicuity
|
1. quality of an object or a light source to appear prominent in its surroundings
2. quality of a sign to attract (attention conspicuity) or gain (search conspicuity) the driver’s attention
|
feltűnőség
|
1. Olyan felület vagy fényforrás, amelynek megjelenése kiemelkedik a háttérből
2. Egy olyan jel minőségét jellemzi, amelynek fel kell kelteni a gépkocsi vezető figyelmét, vagy amely segíti, hogy megkeressen valamit.
|
|
surface colour
|
colour perceived as belonging to a surface from which the light appears to be diffusely reflected or radiated
|
felület szín
|
Színészlelet, amely egy olyan felülethez tartozik, amely a fényt diffúzan veri vissza, vagy diffúzan bocsátja ki.
|
|
light
|
1. characteristic of all sensations and perceptions that is specific to vision
2. radiation that is considered from the point of view of its ability to excite the human visual system
NOTE 1 This term has 2 meanings that should be clearly distinguished. When necessary to avoid confusion between these 2 meanings the term “perceived light” may be used in the first sense.
NOTE 2 Light is normally, but not always, perceived as a result of the action of a light stimulus on the visual system.
|
Fény(észlelet)
|
1. A látási rendszerrel kapcsolatos minden észlelésnek és érzékelésnek univerzális és alapvető jellemzője.
2. minden olyan elektromágneses sugárzás, amely az emberi látó rendszerrel érzékelhető
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ez a definició két gondolatot tartalmaz, amelyeket világosan meg kell különböztetni.
Ha szükséges, az első értelemben az "érzékelt fény" kifejezést lehet használni.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A fény általában – bár nem mindig - a fényinger hatása a látási rendszerre.
|
|
flicker index
|
See NOTE 2 to “amplitude of fluctuation of the luminous flux”
|
Fényáram ingadozási index
|
Lásd 2. MEGJEGYZÉS „a fényáram ingadozásának amplitudója”-nál
|
|
source
|
object that produces light or other radiant flux
|
fényforrás, sugárforrás
|
felület, amely fényt vagy más sugárzást bocsát ki.
|
|
luminance threshold
|
lowest luminance of a stimulus which enables it to be perceived
Unit: cd·m-2
NOTE The value depends on field size, surround, state of adaptation, methodology, and other viewing conditions.
|
Fénysűrűség küszöb
|
A legkisebb érzékelhető fénysűrűség. Mértékegysége: cd·m-2
MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ez az érték függ a látómező méretétől, a környezettől, az adaptációs állapottól és a látás más körülményeitől,
|
|
light pollution
|
generic term indicating the sum total of all adverse effects of artificial light
|
fényszennyezés
|
általános kifejezés amely a mesterséges fény káros hatásainak összegét jelenti
|
|
photopic vision
|
vision by the normal eye in which cones are the principle active photoreceptors
NOTE 1 Photopic vision normally occurs when the eye is adapted to levels of luminance of at least 5 cd·m-2.
NOTE 2 Colour perception is typical of photopic vision.
|
fotopikus látás
(nappali látás)
|
a normál szem látása, amely szemben alapvetően a csapok vannak aktív állapotban
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A nappali látás akkor áll fenn, ha a szem a legalább 5 cd·m-2 megvilágításhoz alkalmazkodik
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A színes látás a nappali látásra jellemző
|
|
man-made sky glow
|
that part of the sky glow which is attributable to man-made sources of radiation (e.g. artificial outdoor lighting)
NOTE Man-made sky glow includes radiation that is emitted directly upwards and radiation that is reflected from the surface of the Earth.
|
Fényszennyezés
|
Az égbolt sugárzásának azon része, amelyet az ember által létrehozott fényforrások okoznak (például mesterségs kültéri világítás).
MEGJEGYZÉS:
Fényszennyezésnek nevezzük azt a sugárzást, amely egyenesen felfelé irányul, és azt is, amelyet a Föld felszíne ver vissza.
|
|
foveola
|
central region of the fovea which contains no blood vessels
NOTE 1 The foveola subtends an angle of about 0,017 rad (1º) in the visual field.
NOTE 2 The central area of the foveola, subtending an angle of about 0,003 rad (0,2º), contains no blue cones.
|
foveola
|
A látógödör középső, legmélyebb része, amelyben csak csapok vannak.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A foveola a látótérnek kb. 0,017 rad (1°) látószögnyi része.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A foveola középső részén mintegy 0,003 rad (0,2º) területen nem találhatók kékérzékeny receptorok.
|
|
vertical illuminance [Ev,v; Ev]
|
illuminance on a vertical plane
Unit: lx = lm·m-2
|
függőleges megvilágítás
[Ev,v; Ev]
|
Megvilágítás a függőleges síkban
Mértékegysége: lx = lm·m-2
|
|
fusion frequency
|
See “critical flicker frequency”
|
Fúziós frekvencia
|
A fényinger változásának az a frekvenciája, amely fölött villogás nem érzékelhető.
|
|
Grassmann’s laws
|
3 empirical laws that describe colour-matching properties of additive colour mixtures of colour stimuli:
to specify a colour match, 3 independent variables are necessary and sufficient,
for an additive mixture of colour stimuli, only their tristimulus values are relevant, not their spectral compositions,
in an additive mixture of colour stimuli, if one or more components of the mixture are gradually changed, the resulting tristimulus values also change gradually
NOTE Grassman’s laws do not hold for all observing conditions.
|
Grassmann törvények
|
Az additív színinger keverés színinger-megfeleltető tulajdonságait leíró három tapasztalati törvény. Ezek a következők:
A színingerek megfeleltetésének jellemzésére három egymástól független változó szükséges és elegendő. Az additív színinger keveréskor csak a színingerek színinger-összetevői számítanak és nem a színingerek spektrális összetétele. Ha a színingerek additív színinger keverésében egy vagy több összetevő színingert folyamatosan változtatnak, akkor a keletkező színinger- összetevők is folyamatosan változnak.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A Grassmann törvények nem érvényesek tetszőleges megfigyelési feltételek mellett.
|
|
threshold increment (disability glare)
|
measure of disability glare expressed as the percentage increase in contrast required between an object and its background for it to be seen equally well with a source of glare present
Unit: 1
NOTE Increasing values of threshold increment correspond to increasing disability glare.
|
határnövekmény
(rontó káprázás)
|
A rontó káprázás mértéke, egy tárgy (amely a káprázás forrása) és a háttér közötti kontraszt növekedésének százalékában kifejezve,
Mértékegysége: 1
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A határnövekmény növekedésének nagysága megfelel a rontó káprázás növekedésének
|
|
Helmholtz-Kohlrausch phenomenon
|
change in brightness of perceived colour produced by increasing the purity of a colour stimulus while keeping its luminance constant within the range of photopic vision
NOTE For related perceived colours, a change in lightness can also occur when the purity is increased while keeping the luminance factor of the colour stimulus constant.
|
Helmholtz-Kohlrausch jelenség
|
A színészlelet világosságának megváltozása, állandó fénysűrűség mellett, a fotopos látás tartományában, ha a színinger tisztasága növekszik.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A nem izolált színészlelet relatív világossága megváltozhat, ha a színinger tisztaság megnövekedik, míg a színérzékleti inger fénysűrűségi tényezője állandó.
|
|
defective colour vision
|
anomaly of vision in which there is a reduced ability to discriminate between some or all colours
NOTE 1 Anomalous trichromatism: Form of trichromatism in which colour discrimination is less than normal.
NOTE 2 Deutan: Adjective denoting deuteranopia or deuteranomaly.
NOTE 3 Deuteranomaly: Defective colour vision in which discrimination of the reddish and greenish contents of colours is reduced, without any colours appearing abnormally dim.
NOTE 4 Deuteranopia: Defective colour vision in which discrimination of the reddish and greenish contents of colours is absent, without any colours appearing abnormally dim.
NOTE 5 Dichromatism: Defective colour vision in which all colours can be matched using additive mixtures of only 2 matching stimuli.
NOTE 6 Monochromatism: Defective colour vision in which all colours can be matched using only a single matching stimulus.
NOTE 7 Protan: Adjective denoting protanopia or protanomaly.
NOTE 8 Protanomaly: Defective colour vision in which discrimination of the reddish and greenish contents of colours is reduced, with reddish colours appearing abnormally dim.
NOTE 9 Protanopia: Defective colour vision in which discrimination of the reddish and greenish contents of colours is absent, with reddish colours appearing abnormally dim.
NOTE 10 Tritan: Adjective denoting tritanopia or tritanomaly.
NOTE 11 Tritanomaly: Defective colour vision in which discrimination of the bluish and yellowish contents of colours is reduced.
NOTE 12 Tritanopia: Defective colour vision in which discrimination of the bluish and yellowish contents of colours is absent.
|
Színtévesztés, színvakság, (hibás színlátás)
|
Látási rendellenesség, amikor bizonyos színekre vagy valamennyi színre csökken az egyén megkülönböztető képessége.
1. MEGJEGZÉS:
Anomális trikromatizmus, (anomális trichromázia), színtévesztés: A trikromatizmus egyik változata, amelynél a szín megkülönböztető képesség a normál színlátóénál kisebb.
2. MEGJEGZÉS:
Deuteranomália: színtévesztés amelyben a színek vöröses és a zöldes tartalma közötti különbség csökkent, anélkül, hogy a többi szín fakóbbnak látszana, és ezt a zöld színre érzékeny receptor (deuteros) hibája okozza.
3. MEGJEGZÉS:
Deuteranópia, színvakság: Színlátási hiba, amelyben a színek vöröses és zöldes tartalma hiányzik, helyettük sárga szín látható, anélkül, hogy bármelyik szín abnormálisan fakónak tűnne, és ezt a zöld színre érzékeny receptor (deuteros) hibája okozza.
4. MEGJEGZÉS:
Protanomália: Színtévesztés amelyben a színek vöröses és a zöldes tartalma közötti különbség csökkent, anélkül, hogy a többi szín fakóbbnak látszana, és ezt a vörösre érzékeny receptor (protos) hibája okozza.
5. MEGJEGZÉS:
Protanópia: Színlátási hiba, amelyben a színek vöröses és zöldes tartalma hiányzik, helyettük sárga szín látható, anélkül, hogy bármelyik szín abnormálisan fakónak tűnne, és ezt a vörösre érzékeny receptor (protos) hibája okozza.
6. MEGJEGZÉS:
Tritanomália: Színtévesztés amelyben a színek kékes és a zöldes tartalma közötti különbség csökkent, anélkül, hogy a többi szín fakóbbnak látszana, és ezt a kékre érzékeny receptor (tritos) hibája okozza.
7. MEGJEGZÉS:
Tritanópia: Színlátási hiba, amelyben a színek kékes és zöldes tartalma hiányzik, helyettük türkiz szín látható, anélkül, hogy bármelyik szín abnormálisan fakónak tűnne, és ezt a kékre érzékeny receptor (tritos) hibája okozza.
8. MEGJEGZÉS:
A tritanomália és a tritanópia rendkívül ritka.
9. MEGJEGZÉS:
Deutan: közös kifejezés a deuteranópia és a deuteranomália megnevezésére.
10. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Protan: közös kifejezés a protanópia és a protanomália megnevezésére.
11. MEGJEGZÉS:
Tritan: közös kifejezés a tritanópia és a tritanomália megnevezésére.
12. MEGJEGZÉS:
Dikromatizmus, dikromázia: Színlátási hiba, amelyben bármely szín egyeztethető mindössze két alapszín additív keverékével (l. Színvakság, 3., 5., 7. MEGJEGYZÉS).
13. MEGJEGZÉS:
Monokromatizmus: Színlátási hiba, amelyben bármely szín egyeztethető egyetlen alapszínnel.
|
|
monochromatism
|
See NOTE 6 to “defective colour vision”
|
Színvakság (hibás színlátás)
|
l. Színvakság
Lásd13. MEGJEGYZÉS a „Színtévesztés, színvakság” címszónál
|
|
invariant wavelengths
|
See NOTE 1 to “Bezold-Brücke phenomenon”
|
Invariáns hullámhossz
|
Lásd 1. MEGJEGYZÉS. a „Bezold-Brücke jelenség” címszónál
|
|
directional effect
|
See “Stiles-Crawford effect (of the first kind)”
|
Irányított emissziós tényező
|
Lásd “Stiles-Crawford effektus” első esete”
|
|
unrelated colour
|
colour perceived to belong to an area seen in isolation from other colours
|
izolált színészlelet
|
Más színektől elkülönített felület által kiváltott színészlelet,
|
|
field of vision
|
extent of space in which objects are visible to an eye in a given position
Equivalent term: “visual field”
NOTE 1 In the horizontal plane meridian the field of vision extends to nearly 190° with both eyes open, the area seen binocularly is about 120°, and the area seen by one eye only is about 154°.
NOTE 2 The extent of the field of vision tends to diminish with age.
|
Látótér
|
Az a térrész, amely egy szem számára egy
adott pozícióban látható
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A horizontális síkban a látótér két nyitott szemmel eléri a közel 190 fokot, binokulárisan pedig közel 120 fok, míg egy szem látótere csak körülbelül 154 fok.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A látótér nagysága a korral kismértékben csökken
|
|
glare
|
condition of vision in which there is discomfort or a reduction in the ability to see details or objects, caused by an unsuitable distribution or range of luminance, or by extreme contrasts
See also “disability glare”, “discomfort glare”
|
káprázás
|
A látás kényelmetlensége és/vagy a tárgyak felismerhetőségének a csökkenése, a fénysűrűség szokatlan eloszlásának vagy szokatlan értékének, illetve a térben vagy időben fellépő igen erős kontrasztnak a következtében.
|
|
glare rating limit [RG,L]
|
maximum allowed value given by the CIE Glare Rating system
Unit: 1
See also CIE 112-1994 Glare Evaluation System for Use within Outdoor Sports- and Area Lighting
Abbreviation: “GRL”
|
Káprázás korlátozási határ
|
A CIE által meghatározott megengedett káprázási határérték
Mértékegysége: 1
Lásd még: CIE 112-1994 „Káprázás kiértékelési rendszer” kültéri és sport megvilágítás esetére
Rövidítés: [RG, L]
|
|
dim (adjective)
|
adjective used to describe low levels of brightness
|
kisfényű
|
a világosság alacsony szintjére használatos megnevezés
|
|
binary hue
|
hue that can be described as a combination of 2 unitary hues
NOTE For example: orange is a yellowish-red or reddish-yellow; violet is reddish-blue, etc.
|
kombinált színezet, kombinált szín
|
Színezet észlelete, amelyet két-két alapszínezet nevének felhasználásával lehet leírni. Például: a narancs sárgás-piros vagy pirosas-sárga; az ibolya pirosas-kék stb.
|
|
complementary wavelength (of a colour stimulus) [λc]
|
wavelength of the monochromatic stimulus that, when additively mixed in suitable proportions with the colour stimulus considered, matches the specified achromatic stimulus
|
Komplementer hullámhossz (szín ingeré)
|
Annak a monokromatikus színingernek a hullámhossza, amely megfelelő arányban additívan keverve a kiválasztott színingerrel a meghatározott akromatikus színingernek felel meg.
|
|
complementary colour stimuli
|
set of 2 colour stimuli for which it is possible to reproduce the tristimulus values of a specified achromatic stimulus by a suitable additive mixture of these 2 stimuli
|
Komplementer színinger
|
Két olyan színinger, amelynek additív keverésével elő lehet állítani egy meghatározott, akromatikus színinger összetevőit.
|
|
contrast
|
1. in the perceptual sense: assessment of the difference in appearance of 2 or more parts of a field seen simultaneously or successively (hence: brightness contrast, lightness contrast, colour contrast, simultaneous contrast, successive contrast, etc.)
2. in the physical sense: quantity intended to correlate with the perceived brightness contrast, usually defined by one of a number of formulae which involve the luminances of the stimuli considered: for example by the proportional variation in contrast near the luminance threshold, or by the ratio of luminances for much higher luminances
|
kontraszt
|
1. Szubjektív: a látómezőkét vagy több, egyidejűleg vagy egymás után látott része közötti megjelenésbéli különbség értékelése (így van: világosságkontraszt, relatív világosságkontraszt, színkontraszt, szimultán kontraszt, szukcesszív kontraszt stb.).
2. Objektív: a világosságkontraszt objektív megfelelője a fénysűrűségkontraszt, amely például a fénysűrűség-küszöb közelében a DL/ L, sokkal nagyobb fénysűrűségek esetében az L1/L2 képlettel határozható meg.
|
|
contrast sensitivity [Sc]
|
reciprocal of the least perceptible (physical) contrast, usually expressed as L/DL, where L is the average luminance and DL is the luminance difference threshold
Unit: 1
NOTE The value of Sc depends on a number of factors including the luminance, the viewing conditions and the state of adaptation.
|
Kontraszt érzékenység
[Sc]
|
A még észlelhető (objektív) kontraszt reciproka, általában L/DL alakban kifejezve, ahol
L az átlagos fénysűrűség és
DL a fénysűrűség-különbség küszöbértéke.
Mértékegysége: 1
MEGJEGYZÉS:
Sc értéke függ a fénysűrűségtől és a látási körülményektől, beleértve az adaptációs állapotot is.
|
|
visual contrast threshold
|
smallest contrast, produced at the eye of an observer by a given object, which renders the object perceptible against a given background
NOTE For meteorological observations, the object must be rendered recognizable, and hence a higher threshold is to be expected. The value of 0,05 has been adopted as the basis for the measurement of meteorological optical range.
|
kontraszt küszöbértéke
|
az a legkisebb kontraszt, amelyet egy megfigyelő észlel egy adott tárgyon,
adott háttér mellett
|
|
proximal field
|
immediate environment of the colour stimulus considered, extending typically for about 2º from the edge of the colour stimulus considered in all, or most, directions
|
közvetlen környezet
|
egy szín inger közvetlen környezete, amely általában a szín inger szélétől 2 fokon belül tetszőleges irányban értendő
|
|
critical flicker frequency
|
for a given set of conditions, the frequency of alternation of stimuli above which flicker is not perceptible
Equivalent term: “fusion frequency”
|
Kritikus flikker frekvencia
|
egy inger változásának frekvenciája adott körülmények között, amikor a villózás (flicker) már éppen nem észlelhető
Azonos értelmű meghatározás: „fúziós frekvencia”
|
|
chroma
|
colourfulness of an area judged as a proportion of the brightness of a similarly illuminated area that appears white or highly transmitting
NOTE For given viewing conditions and at luminance levels within the range of photopic vision, a colour stimulus perceived as a related colour, of a given chromaticity and from a surface having a given luminance factor, exhibits approximately constant chroma for all levels of illuminance except when the brightness is very high. In the same circumstances, at a given level of illuminance, if the luminance factor is increased, the chroma usually increases.
|
kroma
|
Egy felület színezetdússága egy hasonlóan megvilágított fehérnek vagy nagyon fényáteresztőnek látszó felületnek a világosságához képest.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
Adott látási körülmények és a fotopos látáshoz tartozó fénysűrűségek mellett egy viszonyított színészleletnek érzékelt, adott színességű és adott fénysűrűségi tényezőjű felülethez tartozó színészlelet krómája minden megvilágítás mellett megközelítően állandó, kivéve ha a világosság igen nagy. Ugyanezen feltételek mellett, adott megvilágítási szinten, ha a fénysűrűségi tényező nő, akkor általában a króma is nő.
|
|
chromatic adaptation
|
visual process whereby approximate compensation is made for changes in the colours of stimuli, especially in the case of changes in illuminants
|
kromatikus adaptáció
|
Adaptáció olyan fényingerek következtében, amelyekben azok relativ spektrális eloszlásai okozzák a jellemző hatást, különösen megvilágítás esetén.
|
|
chromatic colour
|
in the perceptual sense: perceived colour possessing hue
NOTE 1.In everyday speech, the word colour is often used in this sense in contradistinction to white, grey or black. The adjective coloured usually refers to chromatic colour.
NOTE 2. in the psychophysical sense: see “chromatic stimulus”
|
kromatikus színészlelet
|
Észlelet értelemben: színészlelet, amelynek van színezete.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A mindennapi szóhasználatban a szín szót gyakran ebben az értelemben használják, szembeállítva a fehérrel, szürkével és feketével. A színes jelző általában kromatikus színészleletre utal.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Pszihofizikai értelemben: lásd „szín inger”
|
|
visual acuity
|
1. qualitatively: capacity for seeing distinctly fine details that have very small angular separation
2. quantitatively: any of a number of measures of spatial discrimination such as the reciprocal of the value of the angular separation in minutes of arc of 2 neighbouring objects (points or lines or other specified stimuli) which the observer can just perceive to be separate
Equivalent term: “visual resolution”
|
látásélesség
|
1. Minőségileg: a szemnek az a tulajdonsága, hogy képes egymástól igen kis látószögre lévő finom részletek megkülönböztetésére.
2. Mennyiségileg: annak a legkisebb, ívpercben mért látószögnek a reciprok éneke, amely alatt látott két szomszédos tárgyat (pontot vagy vonalat) a szem még elkülönítve képes észlelni.
Azonos értelmű definíció: „a látás feloldása”
|
|
visual sensation
|
response of the visual system to stimulation
|
látási érzéklet
|
a látórendszer válasza a látási ingerre
|
|
visual task
|
visual elements of the work being done
NOTE The main visual elements are the size of the structure, its luminance, its contrast against the background and its duration.
|
látási feladat
|
Az elvégzendő feladat látással kapcsolatos elemei
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A legfontosabb látási elemek egy struktúra mérete, annak világossága vagy kontrasztja a háttérhez képest, és annak időtartama
|
|
visual resolution
|
See “visual acuity”
|
látóélesség
|
Lásd: „látás élesség”
|
|
fovea
|
central part of the retina, thin and depressed, which contains almost exclusively cones and forming the site of most distinct vision
Equivalent term: “fovea centralis”
NOTE The fovea subtends an angle of about 0,087 rad (5º) in the visual field.
|
Látógödör, fovea
|
A retina középső, vékony és benyomódott része, amely majdnem kizárólag csapokat tartalmaz és a legélesebb látás helye.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A látógödőr a látótérnek kb. 0,087 rad (5°) látószögnyi része.
|
|
visual angle
|
angle subtended by an object or detail at the point of observation
NOTE The SI unit for the angle is rad although it may also be measured in milliradians, degrees, or minutes of arc.
See also “angular subtense”
|
látószög
|
egy tárgy láthatóságának kiterjedése a megfigyelési pont körül
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A szög SI mértékegység radián, és milliradban vagy szögpercben mérhető
|
|
visibility (of a sign)
|
range of visual perception, normally measured in terms of the threshold distance at which a sign becomes visible
|
látótávolság (meteorológiai)
|
a látási észlelés mértéke, amely azon távolságban mérhető, amelyben egy tárgy láthatóvá válik
|
|
viewing flare
|
veiling glare that is observed in a viewing environment but not accounted for in measurements made using a prescribed measurement geometry
NOTE The viewing flare is expressed as a percentage of the luminance of adapted white.
|
látszólagos fátyolfény
|
fátyol tükröződés amely egy megjelenítési környezetben figyelhető meg, de nem mutatható ki méréssel az előírt mérési geometria alkalmazásával
MEGJEGYZÉS A látszólagos fátyolfény az adaptációs fehér százalékában van kifejezve
|
|
macula lutea
|
layer of photostable pigment covering parts of the retina in the foveal region
Equivalent term: “yellow spot”
|
macula lutea
|
a retina fényérzékeny pigmentekkel borított rétege a foveális régióban
|
|
secondary light source
|
surface or object which is not self-emitting but receives light and re-directs it, at least in part, by reflection or transmission
|
másodlagos fényforrás
|
Olyan felület vagy test, amely maga nem bocsát ki fényt, csupán a ráeső fényt vagy annak egy részét áteresztéssel vagy visszaveréssel sugározza tovább.
|
|
corresponding colour stimuli
|
pairs of colour stimuli that have same colour appearance when one is seen in one set of adaptation conditions and the other is seen in a different set
|
Megfeleltetett színingerek
|
olyan szín-inger pár, amely azonos színezetűnek látszik, miközben az egyik egy adott adaptációs környezetben, a másik egy attól eltérő adaptációs környezetben látható
|
|
appearance
|
1. aspect of visual perception by which things are recognized
2. in psychophysical studies, visual perception in which the spectral and geometric aspects of a visual stimulus are integrated with its illuminating and viewing environment
|
megjelenés
|
1. a vizuális észlelésnek egy formája, amely mellett megfigyeljük a tárgyakat
2. pszichofizikai szempontból olyan vizuális észlelés, amelyben a vizuális inger tulajdonságai spektrális és geometriai jellemzői együtt hatnak a megvilágító és látszó környezettel
|
|
appearance model, single-stimulus
|
mathematical model which uses information about viewing conditions to estimate the subjective appearance of a coloured patch from colorimetric measurements of that patch and its surround
NOTE The information about viewing conditions includes the adopted white point.
|
megjelenési modell (egyetlen inger esetén)
|
matematikai modell, amely a látvány körülményeinek információját dolgozza fel annak érdekében, hogy színmérés segítségével becslést adjon egy színes foltnak és környezetének a szubjektív színmegjelenéséről
MEGJEGYZÉS a látvány körülményeinek információja tartalmazza az elfogadott fehér pontot.
|
|
uniformity ratio of illuminance (on a given plane)
|
See “illuminance uniformity”
|
megvilágítás egyenletessége (egy adott síkban)
|
Lásd „Megvilágítás egyenletessége”
|
|
threshold of illuminance
|
smallest illuminance (point brilliance), produced at the eye of an observer by a light source seen in point vision, which renders the source perceptible against a background of given luminance, where the illuminance is considered on a surface element that is normal to the incident rays at the eye
Equivalent term: “visual threshold”
NOTE For visual signalling, the light source must be rendered recognizable, and hence a higher threshold of illuminance is to be expected.
|
megvilágítás küszöbértéke
|
az a legkisebb megvilágítás (pontfény), amelyet egy megfigyelő szeme észlel egy olyan fényforrás esetén amely a látótér egy pontjában egy olyan felületeleme, amely merőlegesnek tekinthető a szembe érkező fénysugárra egy adott megvilágítású hatter előtt
Egyenértékű meghatározás: “láthatósági küszöb”
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A fényjelzőberendezéseknél a fényforrásnak kell felismerhetőnek lenni, és így egy magasabb megvilágítási küszöböt kell elfogadni
|
|
visual threshold (in point vision)
|
See “threshold of illuminance”
|
megvilágítási küszöb
|
Lásd „megvilágítás küszöbértéke”
|
|
illuminant mode (of colour appearance)
|
colour seen as ascribed to a source of illumination
|
megvilágítás mód
(a megvilágítás színe)
|
a fényforrás színének tulajdonított szín
|
|
illuminant
|
radiation with a relative spectral power distribution defined over the wavelength range that influences object colour perception
NOTE In everyday English this term is not restricted to this sense, but is also used for any kind of light falling on a body or scene.
|
Megvilágító (sugárzáseloszlás)
|
sugárzás, amelynek relatív spektrális teljesítmény eloszlása befolyásolja a tárgyak szín észleletét
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A köznapi szóhasználatban ez a fogalom nem korlátozódik erre az egyetlen esetre, hanem minden olyan esetre alkalmazzák, amikor fény esik egy testre vagy egy látványra
|
|
metameric colour stimuli
|
spectrally different colour stimuli that have the same tristimulus values in a specified colorimetric system
Equivalent term: “metamers”
NOTE 1 The corresponding property is called “metamerism”.
NOTE 2 In German, colours (“Farbvalenzen”) consisting of spectrally identical colour stimuli are described as “unbedingt-gleich”.
|
metamer színinger, metamer
|
Olyan spektrálisan különböző színingerek, amelyeknek ugyanazok a színinger-összetevői.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ezt a tulajdonságot metameriának nevezik.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A németben azokat a színingereket („Farbvalenzen”), amelyek spektrálisan megegyező szín ingerekből állnak, Unbedingt-gleichnek nevezik.
|
|
metamers
|
See “metameric colour stimuli”
|
metamerek
|
Lásd „metamer színinger”
|
|
metamerism
|
See NOTE 1 to “metameric colour stimuli”
|
metamerizmus
|
Lásd 1. MEGJEGYZÉS a „metamer színinger” -nél
|
|
metamerism index
|
degree of colour mismatch, calculated in the form of a colour difference, caused by substituting a test illuminant (observer) of different relative spectral composition (responsivity) for the reference illuminant (observer)
NOTE The colour difference is evaluated using a CIE colour difference formula and it must be clearly stated which formula has been used.
|
metameria index
|
A szín eltérés mértéke, amelyet azon színkülönbségként számolunk ki, amely egy referencia megvilágítás (vagy referencia megfigyelő) és az adott megvilágítás (adott megfigyelő) különbségéből ered
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A színkülönbséget a CIE színkülönbségi formulából kell meghatározni, és világosan meg kell adni, hogy melyik formulát használtuk.
|
|
mesopic vision
|
vision by the normal eye intermediate between photopic and scotopic vision
NOTE In mesopic vision, both the cones and the rods are active.
See also CIE 191:2010 Recommended System for Mesopic Photometry based on Visual Performance
|
mezopos látás
|
A fotopos és a szkotopos látás tartományai közötti látás.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A mezopos látásban a csapok és a pálcikák egyaránt működnek.
|
|
daylight locus
|
locus of points in a chromaticity diagram that represents the chromaticities of phases of daylight given by the CIE formulae for daylight illuminants (D illuminants) with different correlated colour temperatures
|
A nappali fény színességi pontjának helye a színességi diagramban
|
A különböző korrelált színhőmérsékletű természetes fény fázisai színességének a helye egy színinger diagramban.
A CIE által meghatározott D65 természetes fény színességének helye különböző korrelált színhőmérsékletek mellett a színességi diagramban.
|
|
daylight illuminant
|
illuminant having the same or nearly the same relative spectral power distribution as a phase of daylight
|
nappali megvilágítás
|
Olyan sugárzáseloszlás, amelynek spektrális teljesítmény eloszlása megegyezik, vagy majdnem megegyezik a természetes nappali fény sugárzáseloszlásával
|
|
related colour
|
colour perceived to belong to an area seen in relation to other colours
|
nem izolált színészlelet
|
Más színekhez viszonyított felület által kiváltott színészlelet.
|
|
non-selective radiator
|
thermal radiator whose spectral emissivity is constant with respect to wavelength over the spectral range considered
|
nem szelektív sugárzás
|
Olyan hőmérsékleti sugárzó, amelynek spektrális emissziós tényezője konstans egy adott hullámhossz tartományban
|
|
readability
|
measure to characterize the ease of reading
|
olvashatóság
|
Olyan mérőszám, amely a könnyű olvashatóságot jellemzi
|
|
optimal colour stimuli
|
object colour stimuli corresponding to objects whose luminance factors have maximum possible values for each chromaticity when their spectral luminance factors do not exceed 1 for any wavelength
NOTE 1 These stimuli correspond, in general, to objects whose spectral luminance factors have values of either unity or 0, with not more than 2 transitions between them.
NOTE 2 The luminance factors and chromaticity coordinates of these stimuli define the boundaries of a colour solid corresponding to non-fluorescent objects.
NOTE 3 For a given luminance factor, these colour stimuli define the maximum purity possible for non-fluorescent objects.
|
optimális színingerek
|
Olyan tárgy-színingerek, amelyeket létrehozó spektrális fénysűrűségi tényezők minden színességhez a legnagyobbak, de értékük egyetlen hullámhosszon sem nagyobb, mint
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ezek az optimális színingerek olyan tárgyakhoz tartoznak, amelyek spektrális fénysűrűségi tényezője vagy 0, vagy 2-nél nem nagyobb.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ezeknek az optimális szín ingereknek a fénysűrűségi tényezői és szín inger-koordinátái határozzák meg a nem fluoreszkáló tárgyakhoz tartozó színtest határait.
3. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Egy meghatározott fénysűrűségi tényezőhöz ezek az optimális színingerek értelmezik a nem fluoreszkáló tárgyak legnagyobb színinger- tisztaságát.
|
|
rods
|
photoreceptors in the retina containing a light-sensitive pigment capable of initiating the process of scotopic vision
|
pálcikák
|
Azok a retinában lévő, fényérzékeny pigmenteket tartalmazó fényérzékelők, amelyek lehetővé teszik a sötétben (szkotopos) látást
|
|
Planckian locus
|
locus of points in a chromaticity diagram that represents chromaticities of the radiation of Planckian radiators at different temperatures
|
Planck sugárzók görbéje
|
A különböző hőmérsékletű Planck sugárzó színességének pontjai a színességi diagramban
|
|
point vision
|
mode of vision, of an apparently small source of light, in which the luminous sensation is determined only by the illuminance that is produced by the source at the eye of the observer
|
pontlátás
|
Olyan látás, melyet egy kicsiny fényforrás vált ki, amelynek fényességét csupán az észlelőben kiváltott fény észlelet alapján határozzuk meg.
|
|
uniform colour space
|
colour space in which equal distances are intended to represent threshold or suprathreshold perceived colour differences of equal size
|
egyenletes színtér
|
Olyan színtér, amelyben azonos színkülönbségekhez azonos távolságok tartoznak
|
|
protan
|
See NOTE 7 to “defective colour vision”
|
protan
|
Lásd 10. MEGJEGYZÉS a „Színtévesztés, Színvakság, (hibás színlátás)” témánál
|
|
protanomaly
|
See NOTE 8 to “defective colour vision”
|
protanomália
|
Lásd 4. MEGJEGYZÉS a „Színtévesztés, színvakság, (hibás színlátás)” témánál
|
|
protanopia
|
See NOTE 9 to “defective colour vision”
|
protanopia
|
Lásd 5. MEGJEGYZÉS a „Színtévesztés, színvakság, (hibás színlátás)” témánál
|
|
Purkinje phenomenon
|
reduction in the brightness of a predominantly long-wavelength colour stimulus relative to that of a predominantly short-wavelength colour stimulus when the luminances are reduced in the same proportion from photopic to mesopic or scotopic levels without changing the respective relative spectral distributions of the stimuli involved
NOTE In passing from photopic to mesopic or scotopic vision, the spectral luminous efficiencies change, the wavelength of maximum efficiency being displaced towards the shorter wavelengths.
|
Purkinje jelenség
|
A világosság észlelet csökkenése a főleg hosszú hullámú tartományba eső színingereknél a főleg rövid hullámú tartományba eső színingerekhez viszonyítva akkor, amikor a megvilágítás csökken, és a fotopikus tartományból a mezopikus tartományba ér, miközben a színinger relatív spektrális eloszlása nem változik.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A fotopikus látásról mezopikusra vagy a scotopikusra történő áttérés során a spektrális fényhatásfok függvény megváltozik, maximumának hullámhossza rövidebb hullámhosszra kerül át.
|
|
basic law of radiometry and photometry
|
See NOTE 7 to “radiance”
|
radiometria és fotometria alaptörvénye
|
Lásd a 7. MEGJEGYZÉS-t a „sugárzás”címszónál
|
|
relative colour stimulus function [ɸ(λ)]
|
relative spectral power distribution of the colour stimulus function
|
relatív színészlelési függvény
|
A színinger függvény relatív spektrális teljesítmény eloszlása.
|
|
adaptation, incomplete
|
phenomenon in which the adopted (computational) white in a given viewing environment does not actually appear white to an observer
NOTE Familiar instances include colour images on newsprint or displays that appear “too yellow or too blue”.
|
részleges adaptáció
|
Jelenség, amelynél az adaptációs (számított) fehér egy adott megfigyelési környezetben nem tűnik teljesen fehérnek egy megfigyelő számára
MEGJEGYZÉS:
hasonló az az eset, amikor a nyomdatechnikában, vagy az újságok színes képein a fehér szín „túl sárgásnak vagy túl kékesnek” tűnik.
|
|
retina
|
membrane situated inside the back of the eye that is sensitive to light stimuli
NOTE The retina contains photoreceptors and nerve cells that interconnect and transmit to the optic nerve the signals resulting from stimulation of the photoreceptors. The photoreceptors in the human retina are of 3 types: rods and cones, which are responsible for vision, and intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs), which play a role in controlling circadian and neuro-endocrine systems.
|
retina
|
A szemgolyó belsejének hátsó felületén lévő, fényingerekre érzékeny hártya
MEGJEGYZÉS:
a retina fényérzékelőket (csapokat és idegvégződéseket) tartalmaz, amelyek a fényérzékelőkben az őket ingerlő fény hatására keletkezett jeleket a látóidegbe vezetik. A humán retina fotoreceptorai 3 félék: pálcikák és csapok, amelyek a látást biztosítják, továbbá olyan fényérzékeny retinális ganglion sejtek (ipRGCs), amelyek szerepet játszanak a circadian és a neuro endokrin rendszer működtetésében.
|
|
sRGB colour space
|
colour space defined by IEC
See also IEC 61966-2-1
|
RGB színtér
|
Az IEC által definiált színtér. Lásd még IEC 61966-2-1
|
|
disability glare
|
glare that impairs the vision of objects without necessarily causing discomfort
|
Rontó káprázás
|
Olyan káprázás, amely rontja a tárgyak látását anélkül, hogy szükségképpen kényelmetlenséget okozna.
|
|
yellow spot
|
See “macula lutea”
|
sárgafolt, macula lutea
|
A látógödör fényérzékeny, sárgán pigmentált rétege.
|
|
dark
|
adjective used to describe low levels of lightness
|
sötét
|
Melléknév, a világosság alacsony szintjének a megjelölésére.
|
|
spectral
|
adjective that, when applied to a quantity X pertaining to electromagnetic radiation, indicates:
either that X is a function of the wavelength λ, symbol: X(λ),
or that the quantity referred to is the spectral concentration of X, symbol: 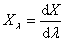
NOTE 1 In the latter case, in French, “spectrique” is preferred to “spectral”.
NOTE 2 Xλ is also a function of λ and in order to stress this, may be written Xλ(λ) without any change of meaning.
NOTE 3 The quantity X can also be expressed as a function of frequency ν, wave number σ, etc.; the corresponding symbols are X(ν), X(σ), etc. and Xν, Xσ, etc.
|
spektrális;
spektral
|
Az elektromágneses sugárzásra vonatkozó valamely X mennyiség jelzője, jelentheti, hogy
— vagy az X a λ, hullámhossz függvénye, jelölése: X(λ),
— vagy az X mennyiség spektrális sűrűsége, jelölése:
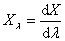
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A „spektrális” szó helyett ajánlható a „spektral” szó alkalmazása
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Xλ azt jelenti, hogy X a λ függvénye. és az Xλ(λ) írásmód még jobban kiemeli ezt.
3. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Az X mennyiség lehet a ν frekvencia vagy a σ hullámszám függvénye is, ebben az esetben megfelelő jelölések X(ν), X(σ), stb lesznek.
|
|
chromaticity coordinates, spectral
|
See “spectral chromaticity coordinates”
|
spektrális színességi koordináták
|
|
|
spectral stimulus
|
See “monochromatic stimulus”
|
monokromatikus szín inger
|
lásd “monochromatic stimulus”
|
|
spectrum locus
|
locus, in a chromaticity diagram or in a tristimulus space, of points that represent monochromatic stimuli
NOTE In tristimulus space, the spectrum locus is a cone that is called in German “Spektralkegel” (“spectral cone”) or, when including the vectors that represent the purple boundary, “Farbtüte”.
|
spektrumgörbe
|
Monokromatikus színingerekhez tartozó pontok helye a színességi-diagramban vagy a trikromatikus színingertérben.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A spektrum görbéje egy kúp a tristimulusos színingertérben, neve a németben Spektralkegel (spectral cone), vagy ha magába foglalja a bíborvonal által reprezentált vektorokat is németül Farbtüte.
|
|
Stiles-Crawford effect (of the first kind)
|
decrease of the brightness of a light stimulus with increasing eccentricity of the position of entry of the light pencil through the pupil
Equivalent term: “directional effect”
NOTE If the variation is in hue and saturation instead of in brightness, the effect is called “Stiles-Crawford effect of the second kind”.
|
Stiles-Crawford effektus
(első esete)
|
A színinger világosságának csökkenése, ha a pupillán belépő fénynyaláb excentricitása növekszik.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ha a változás színezetben és telítettségben van és nem világosságban, akkor ez a második Stiles-Crawford hatás.
|
|
illuminant colorimetric shift
|
change in chromaticity and luminance factor of an object colour stimulus caused by a change in illuminant
|
Sugárzáseloszlás okozta színmérési eltolódás
|
Egy színinger színezetének és világosságának megváltozása a megvilágítás megváltozásának hatására
|
|
illuminant colour shift
|
change in the perceived colour of an object caused solely by change of illuminant in the absence of any change in the observer’s state of chromatic adaptation
|
Sugárzáseloszlás okozta színészlelet eltolódás
|
Tárgy észlelt színességében és fénysűrűségi tényezőjében bekövetkező változás, amelyet a megvilágítás megváltozása okoz, miközben a megfigyelő színadaptációs állapota változatlan
|
|
field colour
|
colour perceived as not belonging to any object
|
Szabad színészlelet
|
Olyan szín észlelet, amelyet semmi nem befolyásol
|
|
color (US)
|
1. (perceived) colour: see “colour (perceived)”
2. (psychophysical) colour: specification of a colour stimulus in terms of operationally defined values, such as 3 tristimulus values
Equivalent term used outside US: “colour”
NOTE 1 When the meaning is clear from the context the term “colour” can be used alone.
NOTE 2 In German “Farbe” is often used instead of “Farbempfindung”. The use of “Farbe” in the sense of “Farbvalenz” should be avoided. It is only when the sense is obvious from the context, or when “Farbempfindung” and “Farbvalenz” are equally suitable, that “Farbe” may be used in the sense of “Farbvalenz”.
|
szín
|
1. lásd “szín észlelet”
2. lásd „pszihofizikai szín”: egy szín inger definiciója 3 tristimulus érték által
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ha a fogalom egyértelmű, akkor a „szín” szó magában alkalmazható
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A német nyelvben gyakran a „Farbe” szót alkalmazzák a “Farbempfindung” helyett.
A “Farbvalenz” szó kerülendő.
|
|
colour
|
|
szín
|
A vizuális észlelés (látás) jellemző tulajdonsága, amely a kromatikus vagy akromatikus tartalom bármilyen kombinációjából tevődhet össze.
Ez a jellemző tulajdonság leírható a kromatikus színek neveivel (sárga, narancs, barna, piros, rózsaszín, zöld, kék, bíbor stb.), az akromatikus színek neveivel (fehér, szürke, fekete stb.)> a színeket minősítve úgy, hogy világos, sötét, viszonylag világos, viszonylag sötét stb. vagy a színek neveinek kombinációjával.
A színészlelet függ a színinger spektrális eloszlásától, a színingerhez tartozó terület méretétől, alakjától, szerkezetétől és környezetétől, a személy látási rendszerének adaptációjától, jártasságától a megfigyelés általános és a hasonló feltételei között.
MEGJEGYZÉSEK:
Ha a szövegből a jelentés egyértelmű, akkor a szín szó önmagában használható.
A színészlelet a színes megjelenés különböző módjai szerint jelentkezhet. A színes megjelenés különböző nevei arra valók, hogy jellemezzék a színész leletek közötti kvalitatív és geometriai különbségeket. A színes megjelenés néhány legfontosabb módjának a neveit a 845-02-19, 20, 21 szakaszok ismertetik.
A színes megjelenés további módjai: a vékonyréteg-színészlelet, a térfogat-színészlelet, a sugárzáseloszlás-színészlelet, a test-színészlelet és a Ganzfeld-színészlelet. A színes megjelenésnek ezek a módjai tovább bővíthetők melléknevekkel, amelyek leírják a színek kombinációját vagy azok tér-, vagy időbeli kapcsolatait. A színészleletek közötti, a különböző színes megjelenéskor keletkező, kvalitatív különbségekre vonatkozó fogalmak a 845-02-22, 23, 24, 25 szakaszokban találhatók.
|
|
chromaticity
|
property of a colour stimulus defined by its chromaticity coordinates, or by its dominant or complementary wavelength and purity taken together
|
szín(esség)
|
A színingernek az a tulajdonsága, amelyet vagy a színinger koordinátáival, vagy jellemző hullámhosszával és a színinger tisztaságával lehet jellemezni.
|
|
colour difference (perceived)
|
perceived dissimilarity between 2 colour elements
See also “CIE 1976 L*a*b* colour difference”, "CIE 1976 L*u*v* colour difference”, "CIELAB colour difference”, "CIELUV colour difference”
|
színkülönbség
|
2 szín észlelet eltérése
Lásd még: “CIE 1976 L*a*b* színkülönbség”, "CIE 1976 L*u*v* színkülönbség”, "CIELAB színkülönbség”, "CIELUV színkülönbség”
|
|
colour atlas
|
collection of colour samples arranged and identified according to specified rules
|
színatlasz
|
Meghatározott szabályok szerint rendezett és megjelölt színes minták gyűjteménye.
|
|
chromaticity diagram
|
plane diagram in which points specified by chromaticity coordinates represent the chromaticities of colour stimuli
NOTE In the CIE standard colorimetric systems y is normally plotted as ordinate and x as abscissa, to obtain an x, y chromaticity diagram.
|
színdiagram
|
Síkban értelmezett diagram, amelyen a színességi koordinátákkal meghatározott pontok képviselik a színingerek színességét.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A CIE szín ingermérő rendszer x, y színességi diagramjában általában az y az ordinátatengely és az x az abszcisszatengely.
|
|
colourfulness
|
attribute of a visual perception according to which the perceived colour of an area appears to be more or less chromatic
NOTE For a colour stimulus of a given chromaticity and, in the case of related colours, of a given luminance factor, this attribute usually increases as the luminance is raised except when the brightness is very high.
|
színezetdússág
|
A vizuális érzékelés jellemző tulajdonsága, amely szerint egy felület színészlelete többé vagy kevésbé kromatikusnak tűnik.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Egy adott kromatikus színészlelési ingernek, ha adott fénysűrűségi tényezőjű viszonyított színészleletről van szó, ez a jellemző tulajdonsága megnő a fénysűrűségi tényező növekedésével, kivéve, ha a világosság nagyon nagy.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A francia „cromie" és az angol „chromaticness" kifejezéseket korábban a színezet és a telítettség együttes észlelésének, vagyis az észlelettel korrelált színezetnek a megnevezésére használták.
|
|
colour equation
|
algebraic or vector representation of the match of 2 colour stimuli, of which, for instance, one may be an additive mixture of 3 reference colour stimuli
Example: [C] ≡ X[X] + Y[Y] + Z[Z]
NOTE 1 In this equation, the sign ≡ indicates a colour match and is read as “matches”. The unbracketed symbols represent the amounts of the stimuli indicated by the bracketed symbols: thus R[R] means R units of stimulus [R], and the sign + means an additive mixture of colour stimuli. In such an equation, a minus sign means that the stimulus is added to those on the other side of the equation when the colour match is made.
NOTE 2 The reference stimuli are represented as [R], [G] and [B] in which case the sign ‘≡’, pronounced “matches” should be used. As an alternative the colour equation can be written using boldface Roman letters when the equal sign ‘=’, pronounced “equals” should be used: C = XX + YY + ZZ.
|
színegyenlet, színingeregyenlet
|
Két színinger megfeleltetésének algebrai vagy vektoros leírása, ahol az egyik színinger például három alapszín-inger additív keverésének az eredménye lehet.
Például: C[C] º X[X\ + Y[Y] + Z[Z]
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A º jel a színinger megfeleltetését jelenti; jelentése: „megfelel”. A zárójelben lévő mennyiség előtti betű a zárójelesen megadott színinger mennyiségét mutatja, vagyis az R[R] kifejezésben R-nyit kell venni az [R] színingerből; és a + jel itt a színingerek additív keverését jelenti. Az ilyen egyenletben a minusz jel azt jelenti, hogy az azt követő színingert az egyenlet másik oldalához kell adni a színingerrel való megfeleltetéskor.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A referencia ingereket [R], [G] és [B] jelöli, és ebben az esetben a ‘≡’ jelen a “megfelel” kifejezést kell érteni. Másik lehetőségként a színinger egyenletet bold görög betűkkel kell írni, és az “=” jelet “egyenlő”-ként kell használni: C=XX+YY+ZZ
|
|
colour-matching
|
action of making a colour stimulus appear the same in colour as a given colour stimulus
NOTE The French term applies mainly to the adjustment of equality of the fields of a visual colorimeter, whereas the English and German terms apply equally well to the selection of 2 material specimens having the same colour under a given illuminant.
|
Szín megfeleltető
|
eljárás, melyben létrehozunk egy színingert, amely színben azonosnak látszik egy adott másik színingerrel
MEGJEGYZÉS:
a francia meghatározás kifejezetten egy vizuális koloriméter mezőinek egyeztetését alkalmazza, míg az angol és a német meghatározás egyaránt 2 anyag féleség összehasonlításáról beszél, amelyek egyforma színűnek látszanak adott megvilágítás mellett.
|
|
colour-matching coefficients
|
3 values of a set of colour-matching functions at a given wavelength
Formerly: “spectral tristimulus values”.
|
Szín megfeleltető együtthatók
|
A 3 szín megfeleltető függvény értéke egy adott hullámhosszon
|
|
colour-matching functions (of a trichromatic system)
|
tristimulus values of monochromatic stimuli of equal radiant power
NOTE 1 The 3 values of a set of colour-matching functions at a given wavelength are called “colour-matching coefficients” (formerly: “spectral tristimulus values”).
NOTE 2 The colour-matching functions may be used to calculate the tristimulus values of a colour stimulus from its colour stimulus functions ɸλ(λ).
See also CIE 15 Colorimetry
See also ISO 11664-1:2007(E)/CIE S 014-1/E:2006 Colorimetry - Part 1: CIE Standard Colorimetric Observers
NOTE 3 In the CIE standard colorimetric systems, the colour-matching functions are represented by the symbols 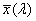 , , 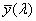 , , 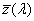 and and 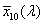 , , 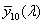 , , 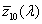 . .
|
Szín megfeleltető függvények (egy trikromatikus rendszerben)
|
Az egyenlő sugárzott teljesítményű monokromatikus színingerek színinger-összetevöi.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Az egy adott hullámhosszhoz tartozó három színinger- megfeleltető függvényt színinger megfeleltető együtthatóknak nevezik (régebben spektrális színinger-összetevőknek hívták).
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A színinger- megfeleltető függvényekkel ki lehet számítani egy színinger szín inger-összetevőit a ɸλ(λ). színinger függvényből
(lásd a CIE 15. sz. kiadványát).
3. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A színinger- megfeleltető függvények jelei a CIE színinger mérő rendszerekben 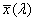 , , 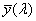 , , 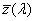 és és 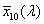 , , 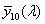 , , 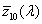 . .
|
|
chromaticity coordinates
|
ratio of each of a set of 3 tristimulus values to their sum
Unit: 1
NOTE 1 As the sum of the 3 chromaticity coordinates is equal to 1, 2 of them are sufficient to define a chromaticity.
NOTE 2 In the CIE standard colorimetric systems, the chromaticity coordinates are represented by the symbols x, y, z and x10, y10, z10.
|
szinességi koordináták
|
A három összetartozó színinger-összetevő mindegyikének és ugyanazon színinger-összetevők összegének a hányadosa.
Megjegyzés :
Mivel a három színességi koordináta összege1, kettő közülük elegendő a színesség jellemzésére.
A színességi koordináták jelei a CIE színinger mérő rendszerekben x, y, z és x10, y10, z10.
|
|
colour (perceived)
|
characteristic of visual perception that can be described by attributes of hue, brightness (or lightness) and colourfulness (or saturation or chroma)
NOTE 1 When necessary, to avoid confusion between other meanings of the word, the term “perceived colour” may be used.
NOTE 2 Perceived colour depends on the spectral distribution of the colour stimulus, on the size, shape, structure and surround of the stimulus area, on the state of adaptation of the observer’s visual system, and on the observer’s experience of the prevailing and similar situations of observation.
NOTE 3 See NOTE 1 and NOTE 2 to “colour”.
NOTE 4 Perceived colour may appear in several modes of colour appearance. The names for various modes of appearance are intended to distinguish among qualitative and geometric differences of colour perceptions. Some of the more important terms of the modes of colour appearance are given in “object colour”, “surface colour” and “aperture colour”. Other modes of colour appearance include film colour, volume colour, illuminant colour, body colour, and Ganzfeld colour. Each of these modes of colour appearance may be further qualified by adjectives to describe combinations of colour or their spatial and temporal relationships. Other terms that relate to qualitative differences among colours perceived in various modes of colour appearance are given in “luminous colour”, “non-luminous colour”, “related colour” and “unrelated colour”.
|
színészlelet
|
A színészlelet 3 jellemzővel írható le: színezet, világosság és színezetdússág.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Szükség esetén annak érdekében, hogy elkerüljük a szó téves értelmezését, alkalmazzuk a színészlelet szót.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A színészlelet függ a színinger spektrális eloszlásától, méretétől, alakjától, struktúrájától és környezetétől, továbbá a megfigyelő vizuális rendszerének adaptációs állapotától, és a megfigyelőnek a hasonló helyzetekben szerzett tapasztalatától.
3. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Lásd az 1. és 2. MEGJEGYZÉS-t a colour címszónál
4. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A színészlelet kifejezés a szín megjelenésének különböző lehetőségeit világítja meg. Az eltérő kifejezések igyekeznek különbséget tenni a színészlelet általános és geometriai sajátságai között. A színmegjelenés legfontosabb tulajdonságait fejezik ki a „tárgy szín”, a „felület-szín”, és az „apertura színészlelet”.
A színes megjelenés további módjai: a vékonyréteg-színészlelet, a térfogat-színészlelet, a sugárzáseloszlás-színészlelet, a test-színészlelet és a Ganzfeld-színészlelet. A színes megjelenésnek ezek a módjai tovább bővíthetők melléknevekkel, amelyek leírják a színek kombinációját vagy azok tér-,vagy időbeli kapcsolatait. A színészleletek közötti, a különböző színes megjelenéskor keletkező, kvalitatív különbségekre vonatkozó fogalmak a 845-02-22, 23, 24, 25 szakaszokban találhatók.
|
|
spot colour
|
single colorant, identified by name, and specified independently from the colour values specified in a trichromatic (colour coordinate) system
|
színezék megnevezése
|
egyszerű szín meghatározás, a trikromatikus (szín koordinátás) színrendszertől függetlenül, a szín nevével határozva meg a színt
|
|
hue
|
attribute of a visual perception according to which an area appears to be similar to one of the colours: red, yellow, green, and blue, or to a combination of adjacent pairs of these colours considered in a closed ring
NOTE Formerly “Farbton” in German. New term is “Buntton”.
|
Színezet
|
A vizuális érzékelés jellemző tulajdonsága, amely szerint úgy tűnik, hogy egy felület hasonlít a piros, sárga, zöld és kék színészlelet egyikéhez vagy közülük a kettő kombinációjához.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A németben régebben; Farbton.
|
|
hue quadrature
|
correlate of hue expressed in terms of the proportions of the unique hues perceived to be present
|
Színezet arányok
|
A színészlelet körülírása az alapszínezetek arányával kifejezve.
|
|
colour temperature [Tc]
|
temperature of a Planckian radiator whose radiation has the same chromaticity as that of a given stimulus
Unit: K
NOTE The reciprocal colour temperature is also used with unit K-1 or MK-1 (where 1 MK-1 = 10-6 K-1) whose previous name “mired” is now obsolete.
|
Színhőmérséklet (korrelált)
|
Egy olyan Planck-sugárzónak a hőmérséklete, amely sugárzásának ugyanaz a színessége, mint a kiválasztott színingeré. Egysége: K
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A reciprok színhőmérséklet megnevezést is használják, egysége K-1.
|
|
colour stimulus
|
visible radiation entering the eye and producing a sensation of colour, either chromatic or achromatic
|
színinger
|
A szembe behatoló és kromatikus vagy akromatikus színészlelést létrehozó látható sugárzás.
|
|
chromatic stimulus
|
stimulus that, under the prevailing conditions of adaptation, gives rise to a chromatic perceived colour
NOTE In the colorimetry of object colours, stimuli having values of purity greater than 0 are usually considered to be chromatic stimuli.
|
színinger (kromatikus)
|
Olyan színinger, amely — általános adaptációs feltételek mellett — kromatikus színészleletet hoz létre.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A tárgy-színészleletek színmérésében, a nullánál nagyobb tisztaságú színingereket általában kromatikus színingereknek minősítik.
|
|
tristimulus values (of a colour stimulus)
|
amounts of the 3 reference colour stimuli, in a given trichromatic system, required to match the colour of the stimulus considered
NOTE In the CIE standard colorimetric systems, the tristimulus values are represented by the symbols R, G, B; X, Y, Z; R10, G10, B10 and X10, Y10, Z10.
|
színinger összetevők
|
Valamely színinger megfeleltetéséhez adott trikromatikus rendszerben szükséges alapszíningerek mennyisége.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A színinger-összetevők jele a CIE színinger méro" rendszerekben: R, G, B; X, Y, Z and X10, Y10, Z10.
|
|
additive mixture of colour stimuli
|
stimulation that combines on the retina the actions of various colour stimuli in such a manner that they cannot be perceived individually
|
színingerek additív keveréke
|
A retina ingerlése több színingerrel úgy, hogy azokat nem lehet külön-külön észlelni.
|
|
colour stimulus function [ɸλ(λ)]
|
description of a colour stimulus by the spectral concentration of a radiometric quantity, such as radiance or radiant power, as a function of wavelength
|
Színinger-függvény
|
A színinger megadása valamelyik radiometriai mennyiség — például a sugársűrűség vagy a sugárzott teljesítmény — spektrális sűrűségének függvényében.
|
|
colour appearance
|
1. aspect of visual perception by which things are recognized by their colour
2. in psychophysical studies: visual perception in which the spectral aspects of a visual stimulus are integrated with its illuminating and viewing environment
|
színmegjelenés
|
1. a látási észlelés egyik fajtája, amelynél a tárgyak a színük által válnak felismerhetővé
2. pszichofizikai tanulmányokban: látási észlelés, amelyben a színinger spektrális jellemzőjét a megvilágítással és a látott környezettel együtt adják meg
|
|
aperture mode (of colour appearance)
|
colour seen through an aperture which prevents its association with a specific object or source
|
apertúra szín észlelés
|
Szín, amely egy apertúrán keresztül látható, amely megakadályozza valamely tárgy vagy fényforrás hatását
|
|
colour appearance model
|
model describing colour appearance, built from descriptors of colour stimuli
NOTE In image processing the following definition is also used: equations and methodologies for transforming physically measurable quantities to and from viewing condition specific perceptual attribute correlates.
|
színmegjelenési modell
|
a színmegjelenés matematikai modellje a színingert leíró tényezők alapján
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A képfeldolgozásban az alábbi definíció is használatos: egyenletek és számítási algoritmusok, a fizikailag mérhető mennyiségek és a látás speciális észlelési jellemzői közötti transzformáció céljára
|
|
colorimetry
|
measurement of colour stimuli based on a set of conventions
|
színmérés
|
Színek mérése meghatározott megállapodások szerint.
|
|
colour space
|
geometric representation of colour in space, usually of 3 dimensions
|
színtér
|
A színingerek geometriai szemléltetése, általában háromdimenziós térben.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A németben a Vektorraum der Farben olyan színinger teret jelent, amelyben a színingereket reprezentáló vektorok kezdőpontjai az akromatikus színérzékelési ingerhez tartozó pontban vannak.
|
|
white point, colour space
|
colour stimulus to which colour space values are normalized
NOTE The colour space white point may or may not correspond to the adapted white point and/or the reference medium white point for a colour image encoding.
|
színtér fehér pontja
|
Szín inger, amelyhez a színtér értékeit normalizálják.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A színtér fehér pontja nem esik egybe az adaptációs fehér ponttal, vagy színes kép referencia felületének fehér pontjával.
|
|
colour solid
|
part of a colour space which contains surface colours
|
színtest
|
A színinger térnek az a része, amely a felületszíneket tartalmazza.
|
|
colorimetric purity [pc]
|
quantity defined by the relation:
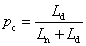
where Ld and Ln are the respective luminances of the monochromatic stimulus and of the specified achromatic stimulus that match the colour stimulus considered in an additive mixture
NOTE 1 In the case of purple stimuli, see NOTE 1 to “purity”.
NOTE 2 In the CIE 1931 standard colorimetric system, colorimetric purity, pc, is related to excitation purity, pe, by the equation pc = pe yd/y where yd and y are the y chromaticity coordinates respectively, of the monochromatic stimulus and the colour stimulus considered.
NOTE 3 In the CIE 1964 standard colorimetric system, a measure, pc,10, is defined by the relation given in NOTE 2, but using pe,10, yd,10 and y10 instead of pe, yd, and y respectively.
|
színtisztaság
|
A következő összefüggéssel értelmezett mennyiség:
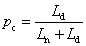
ahol
Ld annak a monokromatikus és
Ln annak a meghatározott akromatikus színingernek a fénysűrűsége, amely additív színinger keveréssel a kiválasztott színingerrel megfeleltethető.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A bíbor színingerekre vonatkozóan 1. a 845-03-46 szakasz 1. megjegyzését.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A CIE 1931 színmérő rendszerben a pc, fénysűrűségi tisztaság és a pe, telítettségi tisztaság között a következő összefüggés van: pc = pe yd/y ahol yd és y a monokromatikus színinger, illetve a kiválasztott színinger y színességi koordinátái.
3. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A CIE 1964 kiegészítő színmérő rendszerben a pc,10 fénysűrűségi tisztaság a 2. megjegyzésben leírt módon van értelmezve, csak a pe, yd, és y helyébe a pe,10, yd,10 értékeket kell írni.
|
|
colour rendering (of a light source)
|
effect of an illuminant on the colour appearance of objects by conscious or subconscious comparison with their colour appearance under a reference illuminant
|
színvisszaadás
|
A sugárzás spektrális eloszlásának a hatása a tárgyak színes megjelenésére; a tárgyak egy referencia-eloszláshoz tartozó színes megjelenésével való tudatos vagy tudatalatti összehasonlítása.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A német nyelv a színvisszaadásra a „Farbwiedergabe" kifejezést használja.
|
|
colour rendering index [R]
|
measure of the degree to which the psychophysical colour of an object illuminated by the test illuminant conforms to that of the same object illuminated by the reference illuminant, suitable allowance having been made for the state of chromatic adaptation
See also CIE 13 Method of Measuring and Specifying Colour Rendering of Light Sources
Abbreviation: “CRI”
|
színvisszaadási index [R]
|
Mérőszám annak jellemzésére, hogy egy vizsgált sugárzáseloszlással megvilágított tárgy színe hogyan egyezik meg ugyanazon tárgynak referencia sugárzáseloszlással történő megvilágításakor kapott színével, figyelembe véve a kromatikus adaptációt.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Lásd még a „Színvisszaadás” címszót
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Lásd még: CIE 13 Method of Measuring and Specifying Colour Rendering of Light Sources
Abbreviation: “CRI”
3. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A német nyelv a színvisszaadási indexre a „Farbwiedergabe-Index" kifejezést használja.
|
|
scotopic vision
|
vision by the normal eye in which rods are the principle active photoreceptors
NOTE 1 Scotopic vision normally occurs when the eye is adapted to levels of luminance of less than ~10-3 cd·m-2.
NOTE 2 In comparison to photopic vision, scotopic vision is characterized by the lack of colour perception and by a shift of the visual sensitivity towards shorter wavelengths.
|
esti látás
|
A néhány század kandela per négyzetméternél kisebb fény sűrűségre adaptált normális szem látása.
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A szkotopikus látás akkor jön létre, ha a szem kisebb, mint ~10-3 cd.m-2 megvilágításra adaptált állapotban van.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A nappali látással összehasonlítva az esti látásra az jellemző, hogy nincs színérzékelés, és a spektrális érzékenység a rövidebb hullámhosszak felé tolódik.
|
|
dispersion
|
1. phenomenon of change in the velocity of propagation of monochromatic radiation in a medium as a function of the frequency of this radiation
2. property of a medium giving rise to this phenomenon
3. property of an optical system resulting in the separation of the monochromatic components of the radiation, obtained for example by means of prisms or gratings
|
szórás
|
1. A monokromatikus sugárzás terjedési sebességének változása valamilyen közegben, a frekvencia függvényében.
2. Valamilyen közegnek az a tulajdonsága, amely az említett jelenséget létrehozza.
3. Valamilyen optikai rendszernek az a tulajdonsága, hogy a sugárzás monokromatikus összetevőit képes elkülöníteni, például prizmákkal vagy rácsokkal.
|
|
Talbot’s law
|
if a point on the retina is excited by a light stimulus that undergoes periodic variations in magnitude at a frequency that exceeds the fusion frequency, the visual perception produced is identical with that produced by a steady stimulus whose magnitude is equal to the mean magnitude of the variable stimulus taken over 1 period
|
Talbot törvény
|
Ha a retina egy részét olyan periodikusan váltakozó fény inger éri, amelynek frekvenciája a fúziós frekvenciánál nagyobb, a létrehozott vizuális észlelés azonos azzal az észleléssel, amelyet a váltakozó fényinger időbeli átlagával meghatározott állandó fény vált ki.
|
|
inherent colour
|
colour perceived to belong to an object irrespective of the illumination and viewing conditions
|
Saját szín
|
Egy tárgyhoz tartozó színészlelet amely független a megvilágítástól és a megfigyelés körülményeitől
|
|
saturation
|
colourfulness of an area judged in proportion to its brightness
NOTE For given viewing conditions and at luminance levels within the range of photopic vision, a colour stimulus of a given chromaticity exhibits approximately constant saturation for all luminance levels, except when the brightness is very high.
|
telítettség
|
Egy felület színdússága a világosságához viszonyítva.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
Adott látási körülmények között és a nappali látási tartományon belüli fénysűrűségi szinteken egy adott színességű színérzékelési inger minden fénysűrűségi szintre állandó telítettségű, kivéve, ha a világosság nagyon nagy.
|
|
volume colour
|
colour perceived as belonging to the bulk of the substance
|
térfogati szín
|
Nagymennyiségű anyaghoz tartozó színészlelet
|
|
natural sky glow
|
that part of the sky glow which is attributable to radiation from celestial sources and luminescent processes in the Earth’s upper atmosphere
|
természetes égbolt sugárzás
|
Az égbolt azon részének sugárzása, amelynek az égbolt ragyogása tulajdonítható, és a Föld felső légköri lumineszcens folyamatainak sugárzása
|
|
natural pupil luminance
|
luminance of a light source (primary or secondary) which, when viewed with the natural pupil, produces the same conventional retinal illuminance, in trolands, as that source viewed with a specified artificial pupil
Unit: cd, cd⋅m-2⋅mm2, troland
|
természetes pupilla fénysűrűség
|
Egy fényforrás sugárzása (elsődleges vagy másodlagos), amelyet egy természetes pupillán át megfigyelve azonos általános retina megvilágítást kapunk, trolandban, mint egy adott fényforrás egy adott mesterséges pupillán keresztül nézve.
Mértékegysége:
cd, cd⋅m-2⋅mm2, troland
|
|
purity (of a colour stimulus)
|
measure of the proportions of the amounts of the monochromatic stimulus and of the specified achromatic stimulus that, when additively mixed, match the colour stimulus considered
NOTE 1 In the case of purple stimuli, the monochromatic stimulus is replaced by a stimulus whose chromaticity is represented by a point on the purple boundary.
NOTE 2 The proportions can be measured in various ways (see “colorimetric purity” and “excitation purity”).
|
tisztaság (színingeré)
|
egy monokromatikus színinger mennyiségének aránya egy meghatározott akromatikus színingerhez, amelyeknek additív keveréke egyező színűnek látszik az adott színingerrel
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Bíbor színinger esetén a monokromatikus inger helyett egy olyan ingert veszünk amelynek a színessége a bíbor vonal megfelelő pontján van.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A mennyiségek különbözőképpen mérhetők, lásd „színtisztaság”, „színinger tisztaság”
|
|
perfect transmitting diffuser
|
diffuser exhibiting isotropic diffuse transmission with a transmittance equal to 1
|
tökéletesen áteresztő diffúzor
|
Ideális egyenletesen szóró közeg, amelynek áteresztési tényezője 1.
|
|
perfect reflecting diffuser
|
diffuser exhibiting isotropic diffuse reflection with a reflectance equal to 1
|
tökéletesen visszaverő diffúzor
|
Ideális egyenletesen szóró közeg, amelynek visszaverési tényezője 1.
|
|
trichromatic system
|
system for specifying colour stimuli in terms of tristimulus values, based on matching colours by additive mixture of 3 suitably chosen reference colour stimuli
|
trikromatikus rendszer
|
Rendszer, amely a színingereket a színinger-összetevőkkel értelmezi; három alkalmasan választott alapszíninger additív színingerkeverésén alapul.
|
|
tritanomaly
|
See NOTE 11 to “defective colour vision”
|
tritanomália
|
Lásd 6. MEGJEGYZÉS a színtévesztés címszónál
|
|
tritanopia
|
See NOTE 12 to “defective colour vision”
|
tritanopia
|
Lásd 7. MEGJEGYZÉS a színtévesztés címszónál
|
|
glare by reflection
|
glare produced by reflections, particularly when the reflected images appear in the same or nearly the same direction as the object viewed
NOTE Formerly: “reflected glare”.
|
Tükröző káprázás
|
Olyan káprázás, amelyet a reflexiók okoznak főként akkor, ha a visszavert képek ugyanabban vagy közel ugyanabban az irányban jelennek meg, mint a szemlélt tárgy.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
Korábban reflected glare.
|
|
chromatic induction
|
modification of the visual response that occurs when 2 colour stimuli (of any spectral irradiance distribution) are viewed side-by-side in which each stimulus alters the appearance of the other
NOTE 1 It is often referred to as simultaneous or spatial contrast because the effect is one of enhancement of colour difference.
NOTE 2 The effect is virtually instantaneous, in contrast to chromatic adaptation which is considered to develop slowly in the visual system.
|
szín kölcsönhatás
|
A szín észlelet módosulása annak következtében, hogy 2 színinger (tetszőleges sugárzás eloszlással) látható közvetlenül egymás mellett, és így mindkét inger módosítja a másik hatását
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ezt gyakran nevezik szimultán vagy térbeli kontrasztnak, mivel ez a jelenség egyike a színkülönbség növekedésének.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ez a hatás gyakorlatilag azonnali, ellentétben a kromatikus adaptációs hatással, amely lassan alakul ki
|
|
colorimetric colour space
|
colour space defined by 3 colorimetric coordinates
NOTE CIE XYZ tristimulus values are colorimetric coordinates, as are RGB values that have an exact and invertible mathematical relationship to CIE XYZ tristimulus values.
|
kolorimetrikus színtér
|
3 színösszetevővel definiált színtér
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A CIE XYZ tristimulus értékek kolorimetriai színösszetevők, éppen úgy mint a CIE RGB értékek, mivel ezek matematikailag átszámítható mennyiségek.
|
|
colorimetric neutral
|
having the same chromaticity as the adopted white
NOTE 1 When stating that an image area is a colorimetric neutral, it is necessary to designate the adopted white. For reflection hardcopy images, the adopted white is typically considered to be either the media white or a perfectly diffuse reflecting surface illuminated by the illumination source.
NOTE 2 The adopted white of colorimetric neutral may or may not correspond to the adapted white according to an observer.
|
kolorimetrikus semleges szín
|
A kolorimetrikus semleges szín adaptációs fehér színe lehet a megfigyelő adaptációs fehér színe is.
|
|
colour boundaries
|
borders of an area in a chromaticity diagram bounded by segments of straight lines
NOTE The area is given either by the equations of the straight lines or by the coordinates of their crossing points between themselves or with the spectrum locus.
|
Szín határok
|
A színességi diagram egy területének egyenes vonalakkal körülzárt határai
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A terület vagy a határvonalak egyenlete által határozható meg, vagy azok egymással vagy a spektrumvonallal létrejövő metszéspontjainak koordinátái által
|
|
colour correction factor
|
no longer in use: see “spectral mismatch correction factor”
|
színkorrekciós faktor
|
A továbbiakban nem használható: lásd „spektrális illesztési korrekció”
|
|
colour element (of a colour appearance model)
|
defined area within which the colour appearance is uniform
|
elemi szín (egy színmegjelenési modellben)
|
Egy adott terület egy egyenközű színmegjelenési modellben
|
|
colour gamut
|
volume, area, or solid in a colour space, consisting of all those colours that are either:
(a) present in a specific scene, artwork, photograph, photomechanical, or other reproduction;
(b) capable of being created using a particular output device and/or medium
NOTE In reproduction and media applications only the volume or solid in a colour space is regarded as colour gamut. In applications such as signal lighting the colour gamut is an area.
|
színtartomány
|
Mennyiség, terület vagy tér rész egy színtérben, amelynek színei vagy:
(a) egy adott színhely, műalkotás, fénykép, fénymásolat vagy egyéb reprodukció részei
(b) alkalmasak arra, hogy létrejőjjenek egy adott kimeneti eszközön és / vagy közegen
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A reprodukciós és média alkalmazások esetében a színtérnek csak a területe vagy térfogata tartozik a színtartományhoz. Egy adott terület szín tartománya olyan alkalmazásoknál, mint például a fényjelek és a megvilágítás.
|
|
colour gamut boundary
|
outer surface of a colour gamut
|
a színtartomány határa
|
A színtartományt körülzáró vonal
|
|
colour order system
|
arrangement of samples according to a set of principles for the ordering and denotation of their colour, usually according to defined scales
NOTE A colour order system is usually exemplified by a set of physical samples, sometimes known as a colour atlas. This facilitates the communication of colour but is not a prerequisite for defining a colour order system.
See also “colour atlas”
|
szín rendszer
|
Minták rendszerezése bizonyos törvényszerűségek alapján, a színük szerint megjelölve őket egy meghatározott skálán
MEGJEGYZÉS:
Egy színrendszert általában egy színminta gyűjteménnyel mutatnak be, amelyet általában Szín Atlasznak neveznek.
Ez megkönnyíti a szín-kommunikációt, de nem előfeltétele a színrendszerbeli meghatározásnak.
Lásd még: "szín atlasz"
|
|
colour patch, test area
|
colour image from an output device or a reflective or transparent hardcopy to be measured, in which the device control values are kept constant within the image area
|
szín minta
|
Egy színes nyomtató kimeneti képe vagy egy reflexiós vagy transzmissziós színes felület, amelynek mért értéke a teljes képmezőben állandó kell legyen.
|
|
afterglow
|
slowly decaying luminescence persisting after the excitation of the luminescent material has ceased, the duration of which may be from about 100 ms to several minutes
|
után-világítás
|
A lumineszkáló anyag gerjesztésének befejezése után lassan lecsengő lumineszkálás, lecsengési ideje 100 ms-tól több percig tarthat.
|
|
illumination
|
application of light to a scene, objects, or their surroundings
Equivalent term: “lighting”
NOTE This term is also used colloquially with the meaning “lighting system” or “lighting installation”.
|
Megvilágítás
|
Fény alkalmazása egy jelenet, tárgy vagy tárgy környezetének megvilágítására.
Egyenértékű kifejezés: "világítás"
MEGJEGYZÉS:
Ezt a kifejezést a köznyelvben is alkalmazzák. A jelentése "világítási rendszer" vagy "megvilágítás".
|
|
lighting
|
See “illumination”
|
világítás
|
Lásd „megvilágítás”
|
|
illumination colour
|
colour perceived as belonging to the light falling on objects
|
megvilágítás színe
|
Szín észlelet amely a tárgyra eső fényre vonatkozik
|
|
illuminating engineering
|
art, science and design of lighting in general, and development of systems for producing, directing, controlling or applying light in particular
|
világítástechnikai tevékenység, fénytechnikai tevékenység
|
Általában a fény művészete, tudománya vagy dekoratív alkalmazása, továbbá olyan rendszerek kifejlesztése, amelyek kimondottan a fény előállítására, irányítására, mérésére vagy alkalmazására szolgálnak
|
|
lighting technology
|
equipment for lighting or its control
See also “illuminating engineering”
|
világítástechnika, fénytechnika
|
Világításra vagy annak mérésére szolgáló berendezés
Lásd még: világítástechnikai tevékenység, fénytechnikai tevékenység
|
|
bright
|
adjective used to describe high levels of brightness
|
világos
|
Melléknév, a világosság magas szintjének a megjelölésére.
|
|
light (adjective)
|
adjective used to describe high levels of lightness
|
világos
|
Melléknév, a relatív világosság nagy szintjének a megjelölésére.
|
|
brightness
|
attribute of a visual perception according to which an area appears to emit, or reflect, more or less light
NOTE The use of this term is not restricted to primary light sources.
|
világosság
|
A vizuális érzékelés jellemző tulajdonsága, amely szerint úgy tűnik, hogy egy felület több vagy kevesebb fényt bocsát ki.
|
|
flicker
|
impression of unsteadiness of visual perception induced by a light stimulus whose luminance or spectral distribution fluctuates with time
|
Villogás
|
A vizuális észlelés ingadozásáról keletkezett benyomás, a fényinger fénysűrűségének vagy spektrális összetételének az időbeni gyors ingadozása által keltett benyomás, ha a változás frekvenciája néhány hertznél nagyobb, de a fúziós frekvencia értékét még nem éri el.
MEGJEGYZÉS:
A magyar szakirodalomban erre a fogalomra az angol flicker illetve a német Flimniem megnevezés is használatos.
|
|
visual perception
|
interpretation of visual sensation
|
látási érzéklet
|
érzékelés a látószerv által
|
|
visual colorimetry
|
colorimetry in which the eye is used to make quantitative comparisons between colour stimuli
|
vizuális kolorimetria
|
olyan kolorimetriai eljárás, amelynek során a színingerek kvantitatív összehasonlítását a szem végzi.
|
|
visual performance
|
quality of performance of the visual system of an observer related to central and peripheral vision
|
vizuális teljesítmény
|
egy megfigyelő látórendszerének teljesítménye a centrális vagy a perifériás látásban
|
|
persistence law, von Kries’
|
See “von Kries’ persistence law”
|
állandósági törvénye, von Kries
|
Lásd: „von Kries állandósági törvénye”
MEGJEGYZÉS:
„szín konstancia” néven is ismert
|
|
von Kries’ persistence law
|
empirical law stating that colour stimuli that match in one set of adaptation conditions continue to do so in any other set
NOTE von Kries’ persistence law does not apply to all conditions.
|
von Kries állandósági törvénye
|
Empirikus törvény, mely kimondja, hogy bizonyos adaptációs körülmények között egyező színingerek tetszőlegesen más adaptációs körülmények között is egyezni fognak
MEGJEGYZÉS:
von Kries állandósági törvénye nem alkalmazható bármely körülmények között
|
|
discomfort glare
|
glare that causes discomfort without necessarily impairing the vision of objects
|
Zavaró káprázás
|
Olyan káprázás, amely kényelmetlenséget okoz anélkül, hogy szükségképpen rontaná a tárgy látását.
|
|
white point
|
achromatic reference stimulus in a chromaticity diagram that corresponds to the stimulus that produces an image area that has the perception of white
|
fehérpont
|
akromatikus referencia inger színpontja egy színességi diagramban, amely egy olyan ingerhez tartozik, amely a fehér szín benyomását kelti
|
|
colour component transfer function
|
single variable, monotonic mathematical function applied individually to one or more colour channels
NOTE 1 Colour component transfer functions are frequently used to account for the non-linear response of a reference device and/or to improve the visual uniformity of a colour space.
NOTE 2 Generally, colour component transfer functions will be non-linear functions such as a power-law (i.e., “gamma”) function or a logarithmic function. However, in some cases a linear colour component transfer function may be used.
NOTE 3 For more information on “colour channels” see NOTE 2 to “colour space encoding”.
|
szín átviteli függvény
|
Egyváltozós, monoton matematikai függvény amelyet egyedileg alkalmazhatunk egy vagy több színcsatornára
1. MEGJEGYZÉS:
A szín átviteli függvény legtöbbször egy referencia eszköz nemlineáris válaszának meghatározására és/vagy egy színtér vízuális egyenletességének javítására alkalmazható.
2. MEGJEGYZÉS:
Alapjában véve a szín átviteli függvény egy nemlineáris függvény, mint például a „gamma-függvény”, vagy egy logaritmikus függvény. Viszont sok esetben lineáris szín átviteli függvényt alkalmaznak.
3. MEGJEGYZÉS:
További információ a szín átviteli függvényről a „Színtér kódolása” címszó 2. MEGJEGYZÉS-ben található
|
|
contrast rendering factor (of a lighting system, for a task)
|
ratio of the contrast of a task under the lighting system considered, to the contrast of the same task under reference lighting
Unit: 1
|
Kontrasztvisszaadási tényező (egy megvilágító rendszer esetén)
|
Egy tárgynak egy adott megvilágítás mellett észlelhető kontrasztjának és ugyanezen tárgynak egy referencia megvilágítás mellett észlelhető kontrasztjának a hányadosa
Mértékegység: 1
|
profile connection space |
colour space used to connect the source and destination profiles in a colour management architecture See also “ICC profile connection space” Abbreviation: “PCS” |
profil összekapcsoló színingertér |
Olyan színingertér, amely a színkezelő architektúrán belül kapcsolatot teremt a forrás és cél profilok között Lásd még: ICC
Rövidítés: PCS |
OECF (abbreviation) |
See “opto-electronic conversion function” |
OECF (betűszó) |
Lásd: optoelektronikai átalakító függvény |
opto-electronic conversion function |
relationship between the log of the input levels and the corresponding digital output levels for an opto-electronic digital image capture system NOTE If the input log exposure points are very finely spaced and the output noise is small compared to the quantization interval, the OECF may have a step-like character. Such behaviour is an artefact of the quantization process and should be removed by using an appropriate smoothing algorithm or by fitting a smooth curve to the data. Abbreviation: “OECF” |
optoelektronikai átalakító függvény |
A bemeneti jelszint logaritmusa és a hozzá tartozó digitális kimeneti jelszint közötti kapcsolat egy optoelektronikus képalkotó eszköz esetében. Megjegyzés: amennyiben a bemeneti fénymennyiség térben nagyon finoman tagolt és a kimeneti zaj kicsi a kvantálási egység felosztásához képest, úgy az OECF lépcsős jellegű is lehet. A lépcsős függvényalak a kvantálás eredménye és eltávolítása megfelelő simító algoritmusokkal vagy görbeillesztési eljárásokkal lehetséges. Rövidítés: OECF |
white point, display illuminant |
point in a chromaticity diagram, which represents the colour of the addition of 100 % of the 3 display primaries measured in a direction perpendicular to the display faceplate |
fehérpont, megjelenítő sugárzó |
A színességi diagram azon pontja amely az alap színingerek 100%-os additív keverékéből áll össze és a képernyőre merőleges irányban mérhető. |
adopted white |
See “white, adopted” |
adaptációs fehérpont |
Lásd: adaptációs fehér |
digital imaging system |
system that records and/or produces images using digital data |
digitális képalkotó rendszer |
Olyan rendszer, amely digitális adatok felhasználásával képes képek rögzítésére és/vagy előállítására |
EOCF (abbreviation) |
See “electro-optical conversion function” |
EOCF (betűszó) |
Lásd: elektrooptikai átalakító függvény |
electro-optical conversion function |
relationship between the digital code values provided to an output device and the equivalent neutral densities produced by the device Abbreviation: “EOCF” |
elektrooptikai átalakító függvény |
Kapcsolatot teremt a kimeneti eszköz digitális értékei és az eszközön megjelenített ekvivalens neutrális denzitás között. Rövidítés: EOCF |
element (of a sign face) |
light emitting or reflective or transmissive component which forms the smallest active part of the sign face NOTE An element may comprise more than 1 emitter. See also “pixel” |
elem (kijelző felületen) |
A kijelző felület legkisebb még aktív sugárzó, áteresztő vagy visszavert fénysugár-komponense Megjegyzés: egy elem több sugárzót is tartalmazhat. Lásd: pixel |
element size (of a sign face) |
diameter of an element Unit: mm |
elem méret (kijelző felületen) |
Az elem átmérője. Mértékegység: mm |
white balance |
adjustment of electronic picture colour channel gains or image processing so that radiation with relative spectral power distribution equal to that of the scene adopted white is rendered as a visual neutral |
fehéregyensúly |
Az elektronikus kép színcsatorna erősítéseinek vagy a képfeldolgozás olyan beállítása, hogy a jelenet fehérpontjának megfelelő relatív spektrális teljesítmény-eloszlással rendelkező fénsugárzással felvett kép fehér adaptációja azonos legyen a neutrális vizuális adaptációval, azaz a sugárzás megfeleljen a semleges látványnak. |
luminance ratio (of a scene or an image) |
ratio of the maximum luminance to the minimum luminance that is either: present in a specific scene, artwork, photograph, photomechanical, or other reproduction; or is capable of being created using a particular output device and medium Unit: 1 |
fénysűrűség-kontrasztarány (jelenet vagy kép esetén) |
A maximális és minimális fénysűrűség aránya egy környezeti beállításon, műalkotáson, fényképen, fotomechanikus vagy más reprodukción vagy más hasonló jellegű kimeneti eszkön vagy médián. Mértékegység: 1 |
luminance contrast ratio (of a display) |
ratio of the luminances of 2 active parts of a display surface having the same or different colours Unit: 1 |
fénysűrűség-kontrasztarány (megjelenítőn) |
két azonos vagy különböző színű aktív részlet fénysűrűség aránya a képernyő felületén. mértékegység: 1 |
film rendering transform |
mapping of image data representing measurements of a photographic negative to output-referred image data representing the colour space coordinates of the elements of a reproduction |
film renderelési átalakítás |
Negatív képek méréssel meghatározott képadatainak leképezése megjelenítőre vonatkozó kimeneti képadatokra, amelyek az alkotás elemeinek színingertérbeli koordinátáiva jellemezhetők. |
liquid crystal display |
a display technology that modulates the light from a backlight to make a grey scale image and uses red, green, and blue colour filters to make a colour image; the modulator consists of a liquid crystal layer that can change the polarization of the light and two (in most cases crossed) polarizers that block the light from the backlight in the off state Abbreviation: “LCD” |
folyadékkristályos kijelző |
Olyan megjelenítési technológia, ahol egy háttérvilágítóbóll származó fényt modulálva keletkezik a szürkeskála kép, majd ezt vörös, zöld illetve kék szűrőkön átvezetve jön létre a színes kép. A modulátor a fény polarizációját változtattó folyadékkristály-rétegből és két (általában egymásra merőleges irányú) polarizációs szűrőből áll, melyek együtt alap állapotban nem fényáteresztők. Rövidítés: LCD |
ICC file format |
file format and encoding used to store transforms that relate one colour encoding with another, in a form defined by the International Color Consortium NOTE For example, the ICC file format can be used to store the transforms used to convert device colour image data to colorimetrically equivalent colour image data, encoded in one of the ICC profile connection colour spaces, as part of a colour management system. The ICC file format specifies a number of transforms to be in each ICC profile file. Equivalent term: "ICC profile format" |
ICC fájlformátum |
Olyan fájlformátum és kódolás, amely az „International Color Consortium” által definiált formában tartalmazza az egyik színkódolásból másikba történő átalakítás eljárásait. Megjegyzés: például a színkezelő rendszer részeként egy összekapcsoló színingertér segítségével az ICC fájlformátum lehetővé teszi egy eszköz képadat kolorimetriailag azonos képadattá történő átalakítását. Az ICC fájlformátum számos átalakítást definiál minden egyes ICC profil fájlban. Azonos terminus: ICC profil formátum |
rendering intent |
style of mapping colour values from one image description to another NOTE Within an ICC profile, a rendering intent identifies the subset of the profile to use for mapping colour values in a particular case. See also "ICC file format" |
renderelési eljárás |
A színinger értékek leképezési módszere két színes képmegadás között. Megjegyzés: Az ICC profilban a renderelési eljárás azonosítja az adott esetre vonatkozó színinger leképzéshez alkalmazandó átalakítási módszert. Lásd még: ICC fájlformátum |
ICC PCS (abbreviation) |
See “ICC profile connection space” |
ICC PCS (betűszó) |
Lásd: ICC profil összekötő színingertér |
ICC profile format |
See “ICC file format” |
ICC profil formátum |
Lásd: ICC fájlformátum |
ICC profile connection space |
colour space encoding used to connect the source and destination transforms (from the source and destination profiles) in the ICC colour management architecture NOTE The ICC.1:2001 specification defines 2 variations of the PCS: a general PCS for colorimetric intent transforms, and an output-referred PCS for perceptual intent transforms. Abbreviation: “ICC PCS” |
ICC profil összekötő színingertér |
Színigertér kódolás, amely a forrás- és cél profilok alapján kapcsolatot teremt a forrás- és a cél átalakítások között az ICC színkezelő rendszerben Megjegyzés: Az ICC 1:2001 előírás két PCS típust határoz meg: általános PCS a kolorimetriai megfeleltetésű átalakításokhoz és megjelenítőre vonatkozó PCS az észleleti megfeleltetésű átalakításhoz.
Rövidítés: ICC PCS |
ISO digital still camera dynamic range |
ratio of the maximum luminance level that appears unclipped to the minimum luminance level that can be reproduced with an incremental signal to temporal noise ratio of at least 1 Unit: 1 NOTE As determined according to ISO 15739 Photography - Electronic still-picture imaging - Noise measurements. |
ISO digitális állókép kamera dinamika tartomány |
A nem levágott maximális- és a minimális fénysűrűségnek az aránya, amely legalább 1 értékű jel és legalább 1 értékű időbeli jel zaj viszonnyal rendelkező zaj aránnyal rendelkezik Egység: 1 Megjegyzés:ahogy az ISO 15739 (Fotográfia – Elektronikus állókép készítés – Zaj mérés) szabvány megadja |
image colour appearance model |
equations and methodologies for transforming physical measurements of the elements of an image to and from viewing condition specific perceptual attribute correlates that estimate the subjective appearance of the elements of the image (cf. colour rendering, different reproduction models, single-stimulus colour appearance model) NOTE 1 An image colour appearance model can be applied to the elements of either a scene, an original, or a reproduction. It determines perceptual attribute correlates for these elements without consideration of the characteristics of any potential medium for subsequent reproduction. However, an image colour appearance model followed by its inverse may be appropriate for use as a colour reproduction model, especially if the reproduction medium does not impose any limitations on the colours to be reproduced in the image. NOTE 2 There is no general consensus on the appropriate form for an image colour appearance model. A single-stimulus colour appearance model cannot be expected to deal completely with the effect of changing viewing conditions in an image because the combined effect of macroscopic viewing conditions and other colours in the image could result in the appearance of any colour in the image changing in a way that is not predictable by the single-stimulus model, since it is not keeping track of the other colours. |
képi színmegjelenítési modell |
Egyenletek és metódusok képek egyes elemein végzett fizikai mérések transzformációiesetén a megtekintési feltételektől függő észleleti korreráltakból és azokba, amelyek közelítőleg megadják a képelemek szubjektív megjelenését (vö. színegyeztetés, eltérő reprodukciós modellek, egyetlen-inger alapú színmegjelenítési modell) 1. megjegyzés: Képi színmegjelenítési modell alkalmazható egy adott jelenet, eredeti, vagy reprodukált kép egyes elemeire. Ez fogja meghatározni az adott elemekészleleti korreráltjait, függetlenül a megjelenítő vagy reprodukció tulajdonságaitól. Egy képi színmegjelenítési modellnek és inverzének összessége bizonyos esetekben kezelhető színegyeztetési modellként, különösen akkor, ha a megjelenítő tulajdonságai nem limitálják a képen megjeleníthető színingereket. 2. megjegyzés: nincs általános egyetértés a képi színmegjelenítési modellek alakjának legmegfelelőbb meghatározására. Az egyetlen-inger alapú színmegjelenítési modelltől nem várható el, hogy tökéletesen alkalmas legyen a változó megtekintési feltételek kezelésére, hiszen a kép egyes részeinek színe és a külső körülmények együttes hatása okozhatnak olyan színmegjelenés-beli eltéréseket, melyeknek leírása az egyetlen-inger alapú modellben – az egyéb színek számontartásának hiányában - nem lehetséges. |
reference medium |
imaging medium associated with a specified real or virtual output device, the characteristics of which are specified as part of the specification of a standard output-referred colour image encoding |
képmegjelenítési referencia |
Leképezés tetszőleges, valós vagy virtuális kimeneti eszközhöz társítva, amelynek jellemzőit a szabványos megjelenítőre vonatkozó színes kép kódolásának specifikációja tartalmazza. |
image state |
attribute of a colour image encoding indicating the kind of image condition inherent in colour image data values prepared and represented in that encoding NOTE 1 Colour image data is “referred” to a particular image condition through image capture, digitization, colour rendering and colour re-rendering processes. NOTE 2 Typical image states are scene-referred, original referred, output referred and picture referred. |
képállapot |
A színes kép kódolásának olyan jellemzője, amely tartalmazza a képi körülményekből származó színadatokra vonatkozó értékeket, így előkészítve és megvalósítva ezen körülmények figyelembe vételét a kódoláskor. 1. megjegyzés: Az egy adott képre vett színinformációk tartalmazzák a kép készítésekor, digitalizálásakor színegyeztetéskor és újra-rendereléskor fellépő körülmények hatásait. 2. megjegyzés: Tipikus képállapotok a jelenetre vonatkozó, eredetire vonatkozó, megjelenítőre és kiegyenlített képre vonatkozó állapotok. |
image state, original-referred |
image state associated with image data that represents the colour space coordinates of the elements of a 2-dimensional hardcopy or softcopy image, typically produced by scanning artwork, photographic transparencies or prints, or photomechanical or other reproductions NOTE 1 When the phrase “original-referred” is used as a qualifier to an object, it implies that the object is in an original-referred image state. For example, original-referred image data are image data in an original-referred image state. NOTE 2 Original-referred image data are related to the colour space coordinates of the original, typically measured according to ISO 13655 Graphic technology - Spectral measurement and colorimetric computation for graphic arts images, and does not include any additional veiling glare or other flare. NOTE 3 The characteristics of original-referred image data that most generally distinguish them from scene-referred image data are that they are referred to a 2-dimensional surface, and the illumination incident on the 2- dimensional surface is assumed to be uniform (or the image data corrected for any non-uniformity in the illumination). NOTE 4 There are classes of originals that produce original-referred image data with different characteristics. Examples include various types of artwork, photographic prints, photographic transparencies, emissive displays, etc. When selecting a colour re-rendering algorithm, it is usually necessary to know the class of the original in order to determine the appropriate colour re-rendering to be applied. For example, a colorimetric intent is generally applied to artwork, while different perceptual algorithms are applied to produce photographic prints from transparencies, or newsprint reproductions from photographic prints. In some cases the assumed viewing conditions are also different between the original classes, such as between photographic prints and transparencies, and will usually be considered in well-designed systems. NOTE 5 In a few cases, it may be desirable to introduce slight colorimetric errors in the production of original-referred image data, for example to make the gamut of the original more closely fit the colour space, or because of the way the image data were captured (such as a Status A densitometry-based scanner). |
képállapot (eredetire vonatkozó) |
Olyan képállapothoz tartozó képi adatok, melyek megadják a kép elemeinek színingertér koordinátáit kétdimenziós nyomtatott, vagy elektronikus formátumok esetén,amelyek lehetnek szkennerrel beolvasott művészi alkotások, fotokópiák, negatívok vagy nyomatok, vagy más fotomechanikus reprodukciók. 1. megjegyzés: amikor az „eredetire vonatkozó” kifejezést alkalmazzuk egy objektum minősítésére, az arra utal, hogy az objektum eredetire vonatkozó képállapotban van. Például az eredetire vonatkozó kép-adataok, egyben az eredetire vonatkozó képállapot adatai is. 2. megjegyzés: az erdetire vonatkozó képadatok az erdeti képanyag színtér koordinátáinak segítségével kerülnek leírásra, melyek megfelelnek az ISO 13655 szabványnak (Graphic technology – Spectral measurement and colorimetric computation for graphic arts images),nem tartalmaznak további káprázási, ill. fátyol adatokat. 3. megjegyzés: az eredetire vonatkozó képállapot jellemzői, amelyek megkülönböztetik a jelenetre vonatkozó képállapottól az, hogy előbbi egyrészt kétdimenziós felületre vonatkoztatott, és a felületre beeső megvilágítás egyenletesnek tekintett (vagy a képadatok a megvilágítás egyenetlenségének megfelelő módon korrigáltak). 4. megjegyzés: Egyes művek típusairól készült eredetire vonatkozó képadatok eltérő jellemzőkkel rendelkeznek. Eltérő típusú művek alatt érthetőek például különböző műalkotások (akvarell, olajfestmény stb.), fotokópiák vagy negatívok továbbá önmagukban fényt kibocsájtó alkotások (pl. fényszobrok, neonreklámok). A megfelelő újrarenderelési algoritmus kiválasztásához így szükséges a mű típusának pontos ismerete, hogy az újraegyeztetés eredménye is megfeleljen az elvárásoknak. Műalkotások esetében például a kolorimetrikus eljárás jellemző, míg fotónyomatok készítése esetén (diákat használva alapanyagként), vagy sajtónyomatok készítésekor (fotonyomatokból kiindulva) más, észlelet mechanizmusokra épülő eljárásokalkalmazottak. Eltérő műtípusok esetében rendszerint eltérő megtekintési feltételek léphetnek fel, elég például fotókópiák vagy diák esetére gondolnunk. Jól megtervezett rendszerek esetében ezen jellemzők figyelembevétele sem maradhat el. 5. megjegyzés: Néhány esetben kívánatos, hogy az erdetire vonatkozó képállapot kialakításakor kismértékű, célzottan definiált színhiba is kódolásra kerüljön. Ezt indokolhatja az, hogy az erdeti mű színtartománya jobban illeszkedjen a színingertérhez, vagy a képadatok rögzítéséhez használt módszer jellegzetességei (például A-típusú denzitometrikus szkenner esetén). |
image state, output-referred |
image state associated with image data that represents the colour space coordinates of the elements of an image that has undergone colour rendering appropriate for a specified real or virtual output device and viewing conditions NOTE 1 When the phrase “output-referred” is used as a qualifier to an object, it implies that the object is in an output-referred image state. For example, output-referred image data are image data in an output-referred image state. NOTE 2 Output referred image data are referred to the specified output device and viewing conditions. A single scene can be colour rendered to a variety of output-referred representations depending on the anticipated output viewing conditions, media limitations, and/or artistic intents. NOTE 3 Output-referred image data may become the starting point for a subsequent reproduction process. For example, sRGB output-referred image data are frequently considered to be the starting point for the colour re-rendering performed by a printer designed to receive sRGB image data. |
képállapot (megjelenítőre vonatkozó) |
Olyan képállapothoz tartozó kép-adatok, melyek reprezentálják egy kép elemeinek színingertér koordinátáit, és amelyek színegyeztetésen mentek keresztül, egy valós vagy virtuális megjelenítő eszköznek és a megtekintési feltételeknek megfelelően. 1. megjegyzés: amikor a "megjelenítőre vonatkozó" kifejezést alkalmazzuk egy objektum minősítésére, az arra utal, hogy az objektum megjelenítőre vonatkozó képállapotban van. Például a megjelenítőre vonatkozó kép-adatok egyben megjelenítőre vonatkozó képállapot adatai is. 2. megjegyzés: a megjelenítőre vonatkozó kép adatok adott megtekintési feltételek mellett egy kimeneti eszközre vonatkoznak. Egyetlen jelenet színegyeztetése a megjelenítőre vonatkozóan igen változatos lehet, a várható kimeneti megtekintési feltételektől, a média korlátoktól, és/vagy művészi eljárásoktól függően. 3. megjegyzés: a megjelenítőre vonatkozó kép-adatok kiindulási pontjai lehetnek egy későbbi reprodukciós folyamatnak. Például, a megjelenítőre vonatkozó sRGB kép-adatok gyakran a nyomtatók által az adatok befogadása érdekében végzett szín újra-egyeztető folyamat kiindulási pontjainak tekinthetők. |
image state, scene-referred |
image state associated with image data that represents estimates of the colour space coordinates of the elements of a scene NOTE 1 When the phrase “scene-referred” is used as a qualifier to an object, it implies that the object is in a scene-referred image state. For example, scene-referred image data are image data in a scene-referred image state. NOTE 2 Scene-referred image data can be determined from raw digital still camera (DSC) image data before colour rendering is performed. Generally, DSCs do not write scene-referred image data in image files, but some may do so in a special mode intended for this purpose. Typically, DSCs write standard output-referred image data where colour rendering has already been performed. NOTE 3 Scene-referred image data typically represent relative scene colorimetry estimates. Absolute scene colorimetry estimates may be calculated using a scaling factor. The scaling factor can be derived from additional information such as the image opto-electronic conversion function (OECF), F Number or Aperture Value, and Exposure Time or Shutter Speed Value tags. NOTE 4 Scene-referred image data may contain inaccuracies due to the dynamic range limitations of the capture device, noise from various sources, quantization, optical blurring and flare that are not corrected for, and colour analysis errors due to capture device metamerism. In some cases, these sources of inaccuracy can be significant. NOTE 5 The transformation from raw DSC image data to scene-referred image data depends on the relative adopted whites selected for the scene and the colour space used to encode the image data. If the chosen scene adopted white is inappropriate, additional errors will be introduced into the scene-referred image data. These errors may be correctable if the transformation used to produce the scene-referred image data is known, and the colour encoding used for the incorrect scene-referred image data has adequate precision and dynamic range. NOTE 6 The scene may correspond to an actual view of the natural world, or may be a computer-generated virtual scene simulating such a view. It may also correspond to a modified scene determined by applying modifications to an original scene to produce some different desired scene. Any such scene modifications should leave the image in a scene-referred image state, and should be done in the context of an expected colour rendering transform. |
képállapot (jelenetre vonatkozó) |
Olyan képállapothoz tartozó kép adatok, melyek egy jelenet elemeinek színtér koordináta becsléseit reprezentálják. 1. megjegyzés: amikor a "jelenetre vonatkozó" kifejezést alkalmazzuk egy objektum minősítésre, az arra utal, hogy az objektum jelenetre vonatkozó képállapotban van. Például a jelenetre vonatkozó kép-adatok egyben jelenetre vonatkozó képállapot adatai is. 2. megjegyzés: a jelenetre vonatkozó képadatok meghatározása nyers (módosítatlan) DSC (Digital Still Camera - digitális fényképezőgép) képadatból még a színegyeztetés előtt történik. A DSC kamerák/fényképezőgépek általában nem írnak a képekbe jelenetre vonatkozó adatokat, de néhány esetben egy külön erre a célra használható módban ez mégis megtörténhet. A DSC-k tipikusan szabványos megjelenítőkre vonatkozó adatokat írnak a képekbe, melyekben a színegyeztetés már megtörtént. 3. megjegyzés: a jelenetre vonatkozó képadatok tipikusan egy relatív jelenet kolorimetriai becsléseit reprezentálják. Az abszolút jelenet kolorimetriai becslései egy skálázási faktor segítségével számíthatók. A skálázási faktor olyan további adatokból származtatható, mint a kép elektrooptikai konverziós függvénye (OECF), rekeszérték vagy F szám, és expozíciós idő vagy shutter/redőnyzár sebesség. 4. megjegyzés: a jelenetre vonatkozó képadatok pontatlanságokat is tartalmazhatnak melyek a képrögzítő eszköz dinamikus tartománybeli korlátainak, különböző zajforrásoknak, kvantálásnak, a korrigálatlan optikai elmosódásoknak és becsillanásoknak, és a képfelvevő eszköz metamériájából adódó színanalizációs hibáknak tudhatók be. Néhány esetben az említett hibaforrások szignifikáns bizonytalanságokat okozhatnak. 5. megjegyzés: a nyers DSC képadat transzformációja jelenetre vonatkozóvá függ az adott jelenethez választott adopted - alkalmazott/számított relatív fehér(pont)től és a képadatok kódoláshoz alkalmazott színtértől. Amennyiben a kiválasztott jelenet adopted fehérje pontatlan, úgy további hibák jelenhetnek meg a képadatokban. Ezen hibákat korrigálni lehet, amennyiben ismert a jelenetre vonatkozó képadatok előállításához használt transzformáció, és a jelenet hibás képadataihoz alkalmazott színkódolás megfelelő pontossággal és dinamikai tartománnyal rendelkezik. 6. megjegyzés: A jelenet megegyezhet/megfelelhet/igazodhat a valós világ látványához, illetve lehet számítógép által generált virtuális jelenet, amely ugyanazt a látványt szimulálja. Megfelelhet továbbá egy módosítani kívánt jelenetnek is, amely az eredeti jeleneten alkalmazott módosítások segítségével állítható elő. Minden ilyen módosításnak jelenetre vonatkozó képállapotban kell hagynia a képet, és egy várható színegyeztetés (transform) keretében kell történnie. |
image state, picture-referred |
image state associated with image data that represents the colour space coordinates of the elements of a hardcopy or softcopy image, encompassing both original-referred image data and output-referred image data NOTE 1 When the phrase “picture-referred” is used as a qualifier to an object, it implies that the object is in a picture-referred image state. For example, picture-referred image data are image data in a picture-referred image state. NOTE 2 Picture-referred image data will generally be colour rendered for a specific real or virtual imaging medium and viewing condition. NOTE 3 Picture-referred image data can include image data that do not originate from an original scene, such as text, line art, vector graphics and other forms of original artwork. |
képállapot (kiegyenlített képre vonatkozó) |
Képállapot (kiegyenlített képre vonatkozó) olyan képállapothoz tartozó kép adatok, melyek reprezentálják egy hardcopy (nyomtatott) vagy softcopy (digitális) kép elemeinek színtér koordinátáit, magukba foglalva mind az eredeti, mind a megjelenítőre vonatkozó kép-adatokat. 1. megjegyzés: amikor a "kiegyenlített képre vonatkozó" kifejezést alkalmazzuk egy objektum minősítésére, az arra utal, hogy az objektum kiegyenlített képre vonatkozó képállapotban van. Például a kiegyenlített képre vonatkozó kép-adatok egyben kiegyenlített képre vonatkozó képállapot adatai is. 2. megjegyzés: a kiegyenlített képre vonatkozó kép-adatok színegyeztetése általában egy adott valós vagy virtuális képalkotó médium és adott megtekintési feltétel szerint történik. 3. megjegyzés: a kiegyenlített képre vonatkozó kép-adatok olyan (kép-) adatokat is tartalmazhatnak, melyek nem az eredeti jelenetből származnak, például szövegek, vektor grafikák, művészi vonalak és az eredeti (mű)alkotások egyéb formái. |
display input/output characteristic |
transfer characteristic relating the normalized digital code value and the normalized output luminance as represented by a mathematical function NOTE The mathematical function is often a power function but may not necessarily be so. |
kijelző bemeneti/kimeneti jellemző |
A normalizált digitális kódérték és a normalizált kimeneti fénysűrűség közötti átviteli karakterisztika, amely matematikai fügvénnyel adható meg. Megjegyzés: A matematikai függvény gyakran hatványfüggvény, de nem feltétlenül az! |
display surface |
part of a display containing elements which may be activated to present visual information NOTE The display surface shall be deemed to include any supplementary front screen materials. |
kijelzőfelület |
A kijelző azon része, amelynek elemein a működtetés során a vizuális információ megjelenik. Megjegyzés:A kijelzőfelület magába foglalja az összes képernyő felületet képező anyagot. |
display surround (in image technology) |
field outside the background, filling the field of vision |
kijelző környezete (képmegjelenítés során) |
A látóteret kitöltő, háttér körüli terület. |
display, flat panel |
display that incorporates a practically flat surface, and is generally much thinner than its diagonal, for the presentation of visual information and whose surface contains an active area consisting of a regular array of electrically alterable, discrete picture elements (pixels) in rows and columns |
kijelző, sík panel |
Vizuális információ megjelenítésére alkalmas elektromos úton változtatható aktív felülettel rendelkező oszlopokba és sorokba szerkesztett aktív képelem mátrix, amely gyakorlatilag teljesen sík képernyő felületet alkot és a vastagsága jóval kisebb a képátlójától . |
ambient white point (of a display) |
chromaticity coordinates representing the lighting in the viewing environment, excluding that from the display, measured in the plane of the display |
környezet fehérpontja (kijelző esetén) |
A képmegjelenítő síkjában, a képernyőn kívűli környezeti világítás színingerkoordinátája, amelynek mérése a megjelenítőtől függetlenül történik. |
ambient illuminance level (of a display) |
illuminance level due to lighting in the viewing environment, excluding that from the display, measured in the plane of the display |
környezet megvilágítási szintje (kijelző esetén) |
A képmegjelenítő síkjában, a képernyőn kívüli kötnyezeti világítás által létrehozott megvilágítás, amelynek mérése a megjelenítőtől függetlenül történik. |
LCD (abbreviation) |
See “liquid crystal display” |
LCD (betűszó) |
Lásd: LCD kijelző |
display, LCD |
multimedia equipment using transmissive or reflective type liquid crystal display to present visual information from analogue and digital inputs |
LCD kijelző |
Olyan multimédia eszköz, amely analóg és digitális bemenetekből jelenít meg vizuális tartalmat transzmissziós vagy reflexiós típusú folyadékkristálos kijelzőn. |
medium white point |
neutral colour with the highest luminance that can be produced by an imaging medium in normal use, measured using the specified measurement geometry |
megjelenítő fehérpontja |
A normál üzemmódban használt képmegjelenítőn, adott geometriával mérhető legnagyobb fénysűrűségű semleges színinger. |
medium black point |
neutral colour with the lowest luminance that can be produced by an imaging medium in normal use, measured using the specified measurement geometry NOTE It is generally desirable to specify a medium black point that has the same chromaticity as the medium white point. |
megjelenítő feketepontja |
A normál üzemmódban használt képmegjelenítőn, adott geometriával mérhető legkissebb fénysűrűségű semleges színinger. Megjegyzés: Általában kívánatos, hogy a megjelenítő feketepontjának színezetét a fehér pontjával azonosként adjuk meg. |
extended gamut |
colour gamut extending outside that of the standard sRGB CRT display gamut NOTE As defined by IEC 61966-2-1 Multimedia systems and equipment - Colour measurement and management - Part 2-1: Colour management - Default RGB colour space - sRGB. |
kiterjesztett színtartomány |
Az sRGB CRT színtartomány kiterjedésénél nagobb színtartomány. Megjegyzés: A következő szabvány szerint: IEC 61966-2-1 Multimedia systems and equipment – Colour measurement and management – Part 2-1: Colour management – Default RGB colour space – sRGB. |
work station |
combination and spatial arrangement of work equipment, surrounded by the work environment under the conditions imposed by the work tasks |
munkaállomás |
A megszabott munkafeladatoknak megfelelő munkaeszköz összeállítás és térbeli elrendezés. |
white, adopted (image capture) |
spectral radiance distribution as seen by an image capture or measurement device and converted to colour signals that are considered to be perfectly achromatic and to have an observer adaptive luminance factor of unity; i.e., colour signals that are considered to correspond to a perfect white diffuser NOTE 1 The adopted white may vary within a scene. NOTE 2 No assumptions should be made concerning the relation between the adapted or adopted white and measurements of near perfectly reflecting diffusers in a scene, because measurements of such diffusers will depend on the illumination and viewing geometry, and other elements in the scene that may affect perception. It is easy to arrange conditions for which a near perfectly reflecting diffuser will appear to be grey or coloured. |
fehérpont (képfelvételnél) |
Olyan spektrális sugárzás eloszlás, amelyet egy képfelvevő eszköz vagy műszer tökéletesen akromatikus színjelekké alakít és a megfigyelő számára a világosság adaptációs faktor egységnyi. Azaz egy tökéletes fehér diffúzornak megfelelő színes jelek összessége. 1. megjegyzés: a fehérpont változhat egy jeleneten belül 2. megjegyzés: adott jelenet beli közel tökéletes diffúzorok esetén nem célszerű mérési összefüggést keresni a fehérpont vagy az adaptációs fehér megállapítására, mivel az ilyen diffúzorok mérése függ a megvilágítástól és a megfigyelés geometriájától, valamint a jelenet más, az észleletet befolyásoló elemeitől. Könnyen előállíthatóak olyan feltételek, amelyek mellett egy közel tökéletes diffúzor szürkének vagy színesnek látszik. |
softcopy |
non-permanent image produced on a device capable of directly representing different analogue or digital images in succession |
nem tartós kép |
Olyan nem állandó kép, amely egy analóg vagy digitális folyamatos közvetlen megjelenítésre alkalmas eszközön kerül bemutatásra. |
pixel |
the smallest element that is capable of generating the full functionality of a display See also “element” |
képelem |
A legkissebb olyan elem, emely a megjelenítő képességeit vissza tudja adni Lásd: elem |
plasma display panel |
type of flat panel display common to large TV displays (32 inches or larger) consisting of a matrix of tiny cells (pixels) between two glass plates holding an inert mixture of noble gases that can be turned into a plasma by applying a voltage across the cell such that the plasma starts emitting electrons, which then excites phosphors to emit light and create a colour image Abbreviation: “PDP” |
plazma megjelenítő felület |
Főleg nagy méretű (32 hüvelykes vagy nagyobb) síkpanel megjelenítők egy típusa, melyekben a színes képmegjelenítés apró cellák(képelemek) mátrixába történik, két üveglap közé zárt villamos feszültséggel plazma állapotba hozott nemesgáz keverék által kibocsájtott elektronok fénypor gerjesztésével Rövidítés: PDP |
PDP (abbreviation) |
See “plasma display panel” |
PDP (betűszó) |
Lásd: plazma megjelenítő panel |
PCS (abbreviation) |
See “profile connection space” |
PCS (betűszó) |
Lásd: profil összekapcsoló színingertér |
spectral basis functions |
set of mathematically decorrelated functions (no function is a linear combination of any of the others) that can be combined to describe the spectral radiances found in a scene or produced using a specified output device and illumination source, or similar functions describing the colour analysis channel responses of an image capture device |
spektrális alapfüggvények |
Matematikailag korrerálatlan függvények csoportja (egyik függvény sem állítható elő a többi lineáris kombinációjaként), amelyekkel le lehet írni egy képben fellelhető vagy meghatározott kimeneti eszközt és fényforrás által előállított spektrális sugárzásokat. Más esetben lehetnek hasonló függvények, melyek egy képrögzítési eszköz színinger-vizsgálati csatorna válaszait írják le. |
normalized (image) signal |
input signal divided by its full-scale value |
normalizált (kép) jel |
A bemeneti- és a teljes jelszint hányadosával megadott mérőszám. |
hardcopy |
self-sustaining image on a solid substrate |
tartós kép (nyomtatott másolat) |
Szilárd hordozóra felvitt tartós kép. |
colour management |
communication of the associated data required for unambiguous interpretation of colour content data, and application of colour data conversions as required to produce the intended reproductions NOTE 1 Colour content may consist of text, line art, graphics, and pictorial images, in raster or vector form, all of which may be colour managed. NOTE 2 Colour management considers the characteristics of input and output devices in determining colour data conversions for these devices. |
színkezelés (színmenedzsment) |
A színinger tartalmi adatainak egyértelmű értelmezéséhez szükséges kapcsolódó adatok kommunikációja, és a szándékolt reprodukáláshoz szükséges színinger adat konverziók felhasználása 1. megjegyzés: A színtartalom állhat szövegből, vonalas grafikából és ábrázolt képből, háló vagy vektor alakban, mindegyik esetben színesen ábrázolva is. 2. megjegyzés: A színkezelés figyelembe veszi a kimeneti és bemeneti eszközök karakterisztikáját ezen eszközök színinger adat konverziójának meghatározásánál. |
corresponding colour reproduction model |
mathematical model that produces transformations, which are applied to scene or original-referred image data to produce image data describing a reproduction, which is as close as possible to being an appearance match to the original NOTE Transformations produced by reproduction models will generally depend on the luminance ratio and colour gamut of the scene or original and the output medium. |
vonatkozó színmegjelenítési modell |
Matematikai modell, amely olyan transzformációkat hoz létre, amelyeket jelenetre vagy eredetire vonatkozó kép-adatokhoz alkalmaznak, hogy képadat leírást állítson elő egy olyan reprodukcióhoz, amely az eredetivel a lehető legnagyobb mértékben azonos megjelenésű. Megjegyzés: A reprodukciós modellek által létrehozott transzformációk általában a jelenet, az eredeti és a megjelenítő fénysűrűség arányától és a színtartományától függenek. |
colour space, device-dependent |
colour space defined by the characteristics of a real or idealized imaging device NOTE Device-dependent colour spaces having a simple functional relationship to CIE colorimetry can also be categorized as colorimetric colour spaces. For example, additive RGB colour spaces corresponding to real or idealized CRT displays can be treated as colorimetric colour spaces. |
színtér, eszközfüggő |
Színtér, melyet egy valós vagy egy idealizált képalkotó eszköz karakterisztikája határoz meg. Megjegyzés: A CIE kolorimetriával egyszerű funkcionális kapcsolatban lévő eszközfüggő színtereket kolorimetrikus színterekként is lehet kategorizálni. Például, a valóságos vagy idealizált CRT monitorokra vonatkozó additív RGB-színtereket kolorimetrikus színterekként kezelhetjük. |
colour reproduction medium |
medium for displaying colour information, e.g. a monitor or a print NOTE For a print, the colour reproduction medium is not the printer but the combination of printer, colorants and substrate. |
színmegjelenítő |
Szín-információ megjelenítésére alkalmas eszköz, például egy monitor vagy egy nyomtató Megjegyzés: nyomtatásnál, a színmegjelenítő nem a nyomtató, hanem, a színezékek, a hordozó és a nyomtató kombinációja. |
film unrendering transform |
mapping of image data representing measurements of a photographic negative to scene-referred image data representing estimates of the colour space coordinates of the elements of the original scene |
film visszarenderelési átalakítás |
A fényképészeti negatív mért jellemzőinek megfelelő adatok leképezése jelenetre vonatkozó kép-adatokká az eredeti jelenet elemeinek színingertérbeli koordinátái becslései alapján. |
preferred reproduction model |
mathematical model that produces transformations which are applied to scene- or original-referred image data to produce image data describing a pleasing reproduction NOTE Preferred reproduction models are different from other reproduction models in that the pleasing reproduction need not be an attempt to reproduce the appearance of the original. In fact, what is considered pleasing may depend on viewer preferences. The transformations produced by a preferred reproduction model are generally dependent on the characteristics of the scene or original and the output medium. |
preferált reprodukciós modell |
Matematikai modell, amely olyan transzformációkat hoz létre, amelyeket jelenetre vagy eredetire vonatkozó képi adatokhoz alkalmaznak, hogy kép adatokat állítson elő egy tetszetős reprodukcióhoz. Megjegyzés: A preferált reprodukciós modellek a többi reprodukciós modelltől abban különböznek, hogy a tetszetős reprodukcióhoz nem szükséges próbát tenni az eredeti megjelenés reprodukálására. Valójában, hogy mit tartanak tetszetősnek, a szemlélő preferenciájától függhet. A transzformációk, melyeket a preferált reprodukciós modellek hoznak létre, általában a jelenet vagy az eredeti karakterisztikájától és a megjelenítőtől függnek. |
multispectral imaging |
See “multispectral image capture” |
multispektrális képalkotás |
Lásd: multispektrális képrögzítés |
imaging, multispectral |
See “multispectral image capture” |
képalkotás (multispketrális) |
Lásd: multispektrális képrögzítés |
multispectral image capture |
image capture with 6 or more broadband sensors Equivalent term: “multispectral imaging” |
multispektrális képrögzítés |
Képrögzítés hat- vagy több szélessávú érzékelővel. Azonos terminus: multispektrális képalkotás |
image capture, multispectral |
See “multispectral image capture” |
képrögzítés, multispektrális |
Lásd: multispektrális képrögzítés |
colour re-rendering |
mapping of picture-referred colour image data appropriate for one specified real or virtual imaging medium and viewing conditions to picture-referred colour image data appropriate for a different real or virtual imaging medium and/or viewing conditions NOTE Colour re-rendering generally consists of one or more of the following: compensating for differences in the viewing conditions, compensating for differences in the dynamic range and/or colour gamut of the imaging media, and applying preference adjustments. |
szín újrarenderelés |
Valós vagy virtuális képmegjelenítő és megjelenítési környezet esetén fenálló képre vonatkozó színadatok leképezése másik valós vagy virtuális képmegjelenítő és/vagy megjelenítési környezet képre vonatkozó színadataira Megjegyzés: a szín újrarendelés általában egy vagy több műveletből áll: a megjelenítési körülmények kompenzációja, a képmegjelenítő dinamikus tartomány- és/vagy a színtartomány-különbségeinek kiegyenlítése, és az előnyös beállítások alkalmazása. |
colour content data |
data consisting of text, line art, graphics, and pictorial images, in raster or vector form |
színtartalmú információ |
Szöveget, vonalas ábrát, grafikát és képet tratalmazó raszteres vagy vektoros adat. |
colour image data, standard original-referred |
defined and documented original-referred colour image data representing the colorimetric coordinates of the colour elements of a two-dimensional hardcopy image produced by scanning artwork, photographic transparencies or prints, or photomechanical or other reproductions See also "image state, original-referred" |
színes kép információ (eredetire vonatkozó) |
Definiált és dokumentált (eredeti forrásra vonatkozó) színes képi információ, amely tartalmazza egy szkennelt kép, egy fotográfiai film vagy más fotomechanikai reprodukció kétdimenziós tartós kép színiger koordinátáit. Lásd: képállapot (jelenetre vonatkozó) |
colour image data, standard output-referred |
output-referred image data, which are referred to a standardized real or virtual output device and viewing conditions NOTE 1 Image data intended for open interchange are most commonly standard output-referred. This is because with standard output-referred image data it is generally sufficient to specify the standard output to which the image data are referred to interpret the colour appearance described by the image data. NOTE 2 Standard output-referred image data may become the starting point for a subsequent reproduction process. For example, sRGB standard output-referred image data are frequently considered to be the starting point for the colour re-rendering performed by a printer designed to receive sRGB image data. See also "image state, output-referred" |
színes képi információ (megjelenítőre vonatkozó) |
Megjelenítőre vonatkozó képi információ, amely egy szabványosított valós vagy virtuális kimeneti eszközre és megjelenítési környezetre vonatkozik 1. megjegyzés: A nyílt adatcserére szánt képi információk leggyakrabban megjelenítőre vonatkozóak. Ez azért van, mivel a szabványos megjelenítőre vonatkozó képi információnál általában elegendő meghatározni a szabványos kimenetet, amelynek képinformációját a képi információ által leírt szín megjelenítéseként értelmezzük. 2. megjegyzés: Szabványos megjelenítőre vonatkozó képi információ kiindulópontja lehet egy későbbi reprodukciós folyamatnak. Például egy sRGB szabvány megjelenítőre vonatkozó képi információ gyakran tekinthető egy sRGB képi információk fogadására alkalmas nyomtató általi szín újrarendelés kiindulópontjának. Lásd: képállapot, megjelenítésre vonatkozó. |
colour image data, standard scene-referred |
defined and documented colour image data representing estimates of the colorimetric coordinates of the elements of a scene. See also "image state, scene-referred" |
színes képi információ (jelenetre vonatkozó) |
Definiált és dokumentált színes képi információ, amely tartalmazza a jelenet színinger koordinátáit. Lásd még: képállapot (jelenetre vonatkozó) |
colour image encoding |
digital encoding of colour values, together with any information necessary to properly interpret the colour values such as the image state, the intended image viewing environment and the reference medium NOTE 1 In some cases the intended image viewing environment will be explicitly defined for the colour image encoding. In other cases, the intended image viewing environment, i.e., details of the image state, may be specified on an image-by-image basis using metadata associated with the digital image. NOTE 2 Some colour image encodings will indicate particular reference medium characteristics, such as a reflection print with a specified density range. In other cases the reference medium will be not applicable, such as with a scene-referred encoding, or will be specified using image metadata. NOTE 3 Colour image encodings are not limited to pictorial digital images that originate from an original scene, but are also applicable to digital images with content such as text, line art, vector graphics and other forms of original artwork. |
színes kép kódolása |
Színinger értékek digitális kódolása bármely olyan információval, amely szükséges a színinger értékek értelmezéséhez, mint például a képállapot, a kép kijelölt megfigyelési környezete és a képmegjelenítési referencia eszköz. 1. megjegyzés: Néhány színes kép kódolás esetén a kép kijelölt megfigyelési környezete külön definiálásra kerül. Más esetekben a kép kiejlölt kódolási környezete, azaz a képállapot részletei minden egyes képnél külön kerülhetnek megadásra a digitális kép metaadatai alapján. 2. megjegyzés: Egyes színes képi kódolások esetén külön megadhatóak a képmegjelenítés referencia eszköz jellemzői. Pl.: adott denzitástartományú reflexiós nyomtatás. Más esetekben a képmegjelenítési referenciaeszköz nem adható meg, mint például jelenetre vonatkozó képi kódolásnál. Előfordulhat, hogy a képi megjelenítési referenciaeszközt a kép metaadatai alapján lehet meghatározni. 3. megjegyzés: A színes képi kódolásokat nem kizárólag olyan digitális képekre lehet alkalmazni, amelyek eredeti jelenetekről készültek. Alkalmazhatók még olyan digitális képekre, amelyek szöveges, vonalas, vektoros vagy egyéb eredeti alkotási formákat tartalmaznak. |
colour space encoding |
digital encoding of a colour space, including the specification of a digital encoding method, and an encoding range NOTE 1 Multiple colour space encodings may be defined based on a single colour space where the different colour space encodings have different digital encoding methods and/or encoding ranges. (For example, 8-bit sRGB and 10-bit e-sRGB are different colour space encodings based on a particular RGB colour space.) NOTE 2 A colour space encoding is defined with a number of colour channels, each channel corresponding to one dimension of the colour space. Encoded colour channel data values indicate a position along the corresponding dimension in the geometric colour space representation. |
színtérkódolás |
Színingertér digitális kódolása, amely tartalmazza a digitális kódolás módszerét és a kódolás tartományát. 1. megjegyzés: Több színinger-kódolási módszert is definiálhatunk ugyanazon színingerteret véve alapul, amely esetben a különböző színingertér-kódolások különböző digitális kódolási módszerekkel készülnek és/vagy különböző kódolási tartományokon érvényesek. (Például a 8-bites sRGB és a 10-bites e-sRGB színingertér-kódolások különbözőek akkor is, ha ugyanazon RGB színingertér alapján készültek.) 2. megjegyzés: A színingertér-kódolásokat színcsatornák megadásával szokás definiálni, ahol az egyes színcsatornák a színingertér egyes dimenzióira vonatkoznak. A kódolt színcsatorna információ-értékek megadják a vonatkozó dimenziók szerinti pozíciókat a színingertér geometriai megjelenítésében. |
colour encoding |
quantized digital encoding of a colour space, encompassing both colour space encoding and colour image encoding |
színingerkódolás |
A színingertér kvantált digitális kódolása, amely magában foglalja a színingertér kódolását és a színes kép kódolását. |
colour image data |
digitally encoded information, with colour aspects represented using a colour image encoding |
színes képi információ |
Digitálisan kódolt információ, melynek színinger tartalmát színes képi kódolással jeleníthetjük meg. |
line separation |
separation between lines of characters expressed in terms of the number of inactive elements or the distance between centres of adjacent character elements of consecutive character lines |
vonalszétválás |
Karaktervonalak közötti szétválás, amelyet kifejezhetünk egyrészt az inaktív elemek számával, másrészt az egymást közvetlenül követő karaktervonalak egymás melletti karakter elemei középpontjai között mért távolsággal. |